U. S. Army on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight
See als
Title 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001
The oldest and most senior branch of the U.S. military in order of precedence, the modern U.S. Army has its roots in the
Journals of the Continental Congress, Volume 27
/ref> The United States Army considers itself to be a continuation of the Continental Army, and thus considers its institutional inception to be the origin of that armed force in 1775. an excerpt from Robert Wright, ''The Continental Army'' The U.S. Army is a uniformed service of the United States and is part of the
Section 7062 of Title 10, U.S. Code
defines the purpose of the army as: * Preserving the peace and security and providing for the defense of the United States, the Commonwealths and possessions and any areas occupied by the United States * Supporting the national policies * Implementing the national objectives * Overcoming any nations responsible for aggressive acts that imperil the peace and security of the United States In 2018, the ''Army Strategy 2018'' articulated an eight-point addendum to the Army Vision for 2028.The Army Strategy
2018 While the Army Mission remains constant, the Army Strategy builds upon the Army's Brigade Modernization by adding focus to Corps and Division-level echelons.
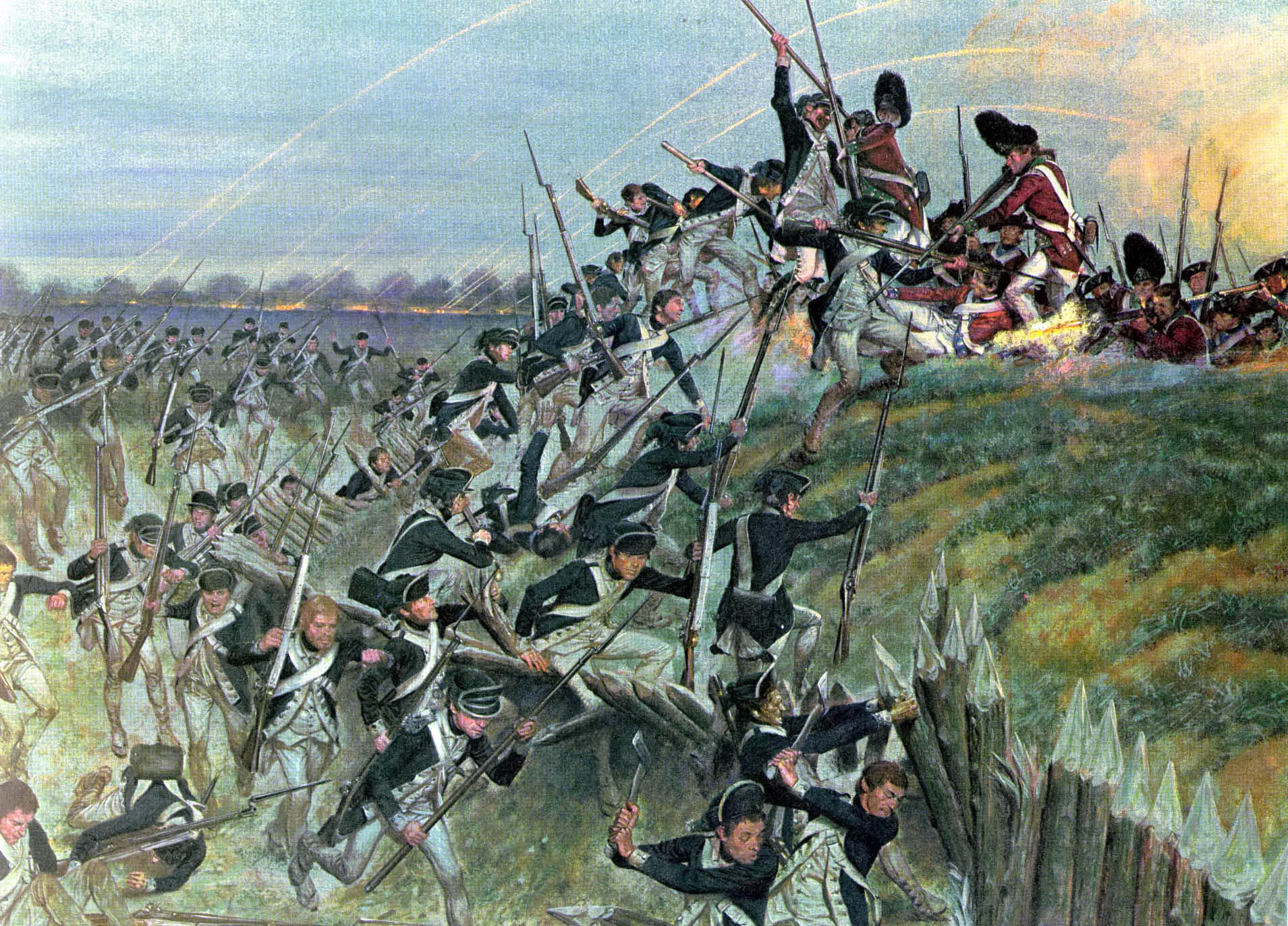 The Army fought numerous pitched battles, and sometimes used Fabian strategy and hit-and-run tactics in the South in 1780 and 1781; Under Major General Nathanael Greene, it hit where the British were weakest to wear down their forces. Washington led victories against the British at Trenton and Princeton, but lost a series of battles in the
The Army fought numerous pitched battles, and sometimes used Fabian strategy and hit-and-run tactics in the South in 1780 and 1781; Under Major General Nathanael Greene, it hit where the British were weakest to wear down their forces. Washington led victories against the British at Trenton and Princeton, but lost a series of battles in the
 The War of 1812, the second and last war between the United States and Great Britain, had mixed results. The U.S. Army did not conquer Canada but it did destroy Native American resistance to expansion in the Old Northwest and it validated its independence by stopping two major British invasions in 1814 and 1815. After taking control of Lake Erie in 1813, the U.S. Army seized parts of western Upper Canada, burned York and defeated Tecumseh, which caused his Western Confederacy to collapse. Following U.S. victories in the Canadian province of Upper Canada, British troops who had dubbed the U.S. Army "Regulars, by God!", were able to capture and burn Washington, which was defended by militia, in 1814. The regular army, however, proved they were professional and capable of defeating the British army during the invasions of Plattsburgh and
The War of 1812, the second and last war between the United States and Great Britain, had mixed results. The U.S. Army did not conquer Canada but it did destroy Native American resistance to expansion in the Old Northwest and it validated its independence by stopping two major British invasions in 1814 and 1815. After taking control of Lake Erie in 1813, the U.S. Army seized parts of western Upper Canada, burned York and defeated Tecumseh, which caused his Western Confederacy to collapse. Following U.S. victories in the Canadian province of Upper Canada, British troops who had dubbed the U.S. Army "Regulars, by God!", were able to capture and burn Washington, which was defended by militia, in 1814. The regular army, however, proved they were professional and capable of defeating the British army during the invasions of Plattsburgh and
 The American Civil War was the costliest war for the U.S. in terms of casualties. After most slave states, located in the southern U.S., formed the Confederate States, the Confederate States Army, led by former U.S. Army officers, mobilized a large fraction of Southern white manpower. Forces of the United States (the "Union" or "the North") formed the Union Army, consisting of a small body of regular army units and a large body of volunteer units raised from every state, north and south, except South Carolina.
For the first two years, Confederate forces did well in set battles but lost control of the border states. The Confederates had the advantage of defending a large territory in an area where disease caused twice as many deaths as combat. The Union pursued a strategy of seizing the coastline, blockading the ports, and taking control of the river systems. By 1863, the Confederacy was being strangled. Its eastern armies fought well, but the western armies were defeated one after another until the Union forces captured New Orleans in 1862 along with the Tennessee River. In the Vicksburg Campaign of 1862–1863, General Ulysses Grant seized the Mississippi River and cut off the Southwest. Grant took command of Union forces in 1864 and after a series of battles with very heavy casualties, he had General
The American Civil War was the costliest war for the U.S. in terms of casualties. After most slave states, located in the southern U.S., formed the Confederate States, the Confederate States Army, led by former U.S. Army officers, mobilized a large fraction of Southern white manpower. Forces of the United States (the "Union" or "the North") formed the Union Army, consisting of a small body of regular army units and a large body of volunteer units raised from every state, north and south, except South Carolina.
For the first two years, Confederate forces did well in set battles but lost control of the border states. The Confederates had the advantage of defending a large territory in an area where disease caused twice as many deaths as combat. The Union pursued a strategy of seizing the coastline, blockading the ports, and taking control of the river systems. By 1863, the Confederacy was being strangled. Its eastern armies fought well, but the western armies were defeated one after another until the Union forces captured New Orleans in 1862 along with the Tennessee River. In the Vicksburg Campaign of 1862–1863, General Ulysses Grant seized the Mississippi River and cut off the Southwest. Grant took command of Union forces in 1864 and after a series of battles with very heavy casualties, he had General
 Following the Civil War, the U.S. Army had the mission of containing western tribes of Native Americans on the
Following the Civil War, the U.S. Army had the mission of containing western tribes of Native Americans on the
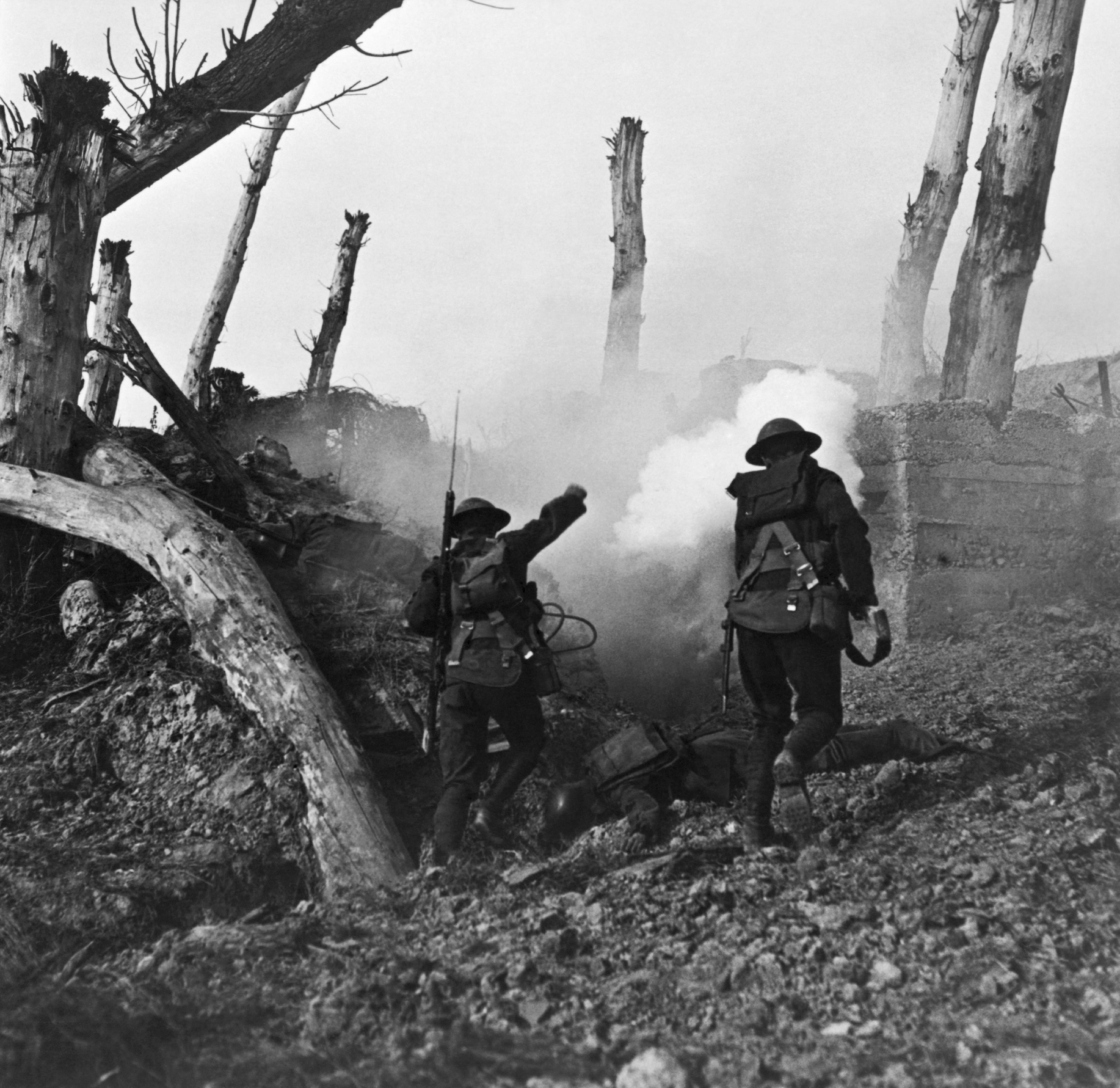 The United States joined World War I as an "Associated Power" in 1917 on the side of Britain, France, Russia, Italy and the other Allies. U.S. troops were sent to the
The United States joined World War I as an "Associated Power" in 1917 on the side of Britain, France, Russia, Italy and the other Allies. U.S. troops were sent to the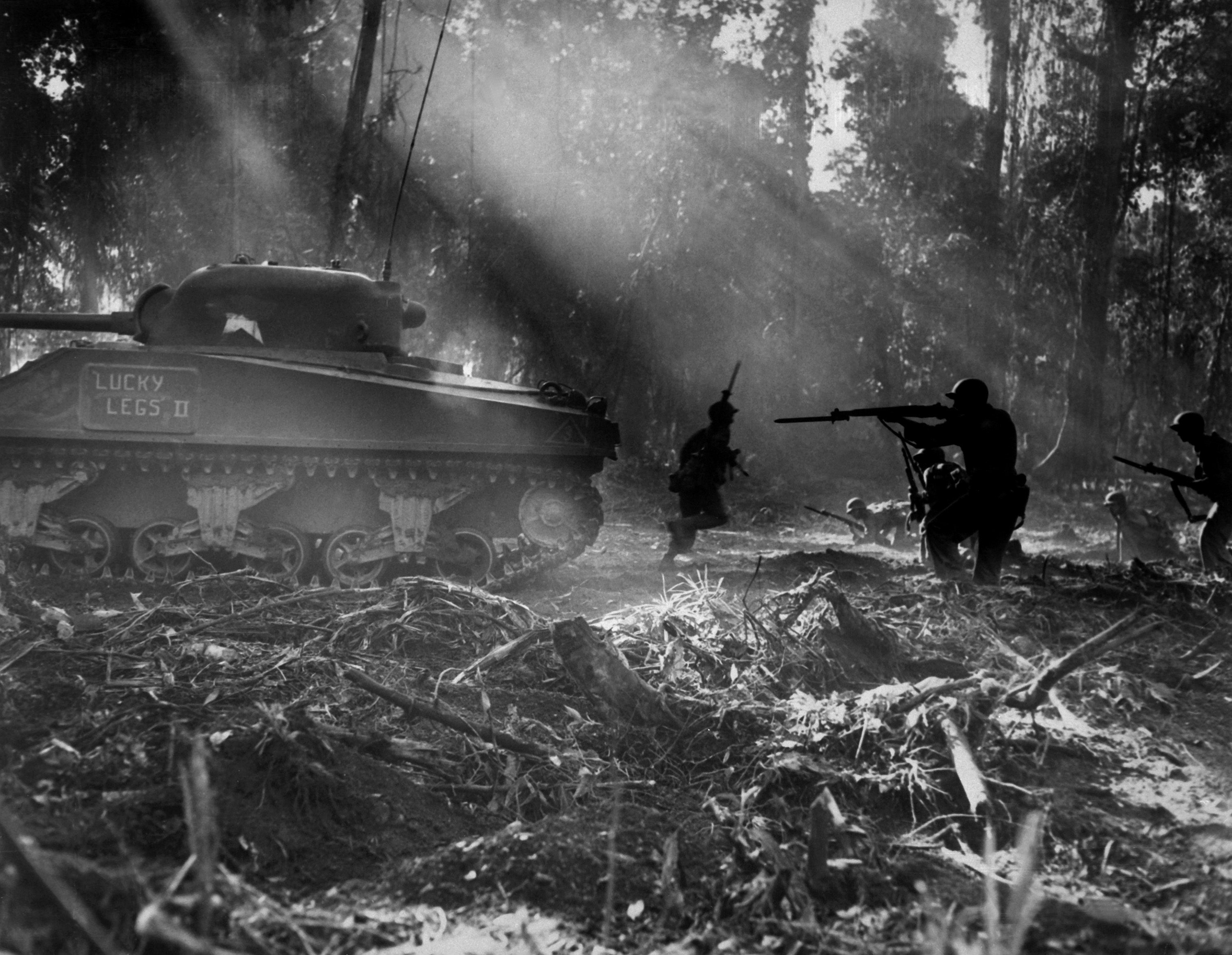  The United States joined World War II in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. Some 11 million Americans were to serve in various Army operations.. Other sources count the Army of Occupation up to 31 December 1946. By 30 June 1947 the Army's strength was down to 990,000 troops. On the European front, U.S. Army troops formed a significant portion of the forces that landed in French North Africa and took Tunisia and then moved on to Sicily and later fought in Italy. In the June 1944 landings in northern France and in the subsequent
The United States joined World War II in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. Some 11 million Americans were to serve in various Army operations.. Other sources count the Army of Occupation up to 31 December 1946. By 30 June 1947 the Army's strength was down to 990,000 troops. On the European front, U.S. Army troops formed a significant portion of the forces that landed in French North Africa and took Tunisia and then moved on to Sicily and later fought in Italy. In the June 1944 landings in northern France and in the subsequent
 The end of World War II set the stage for the East–West confrontation known as the
The end of World War II set the stage for the East–West confrontation known as the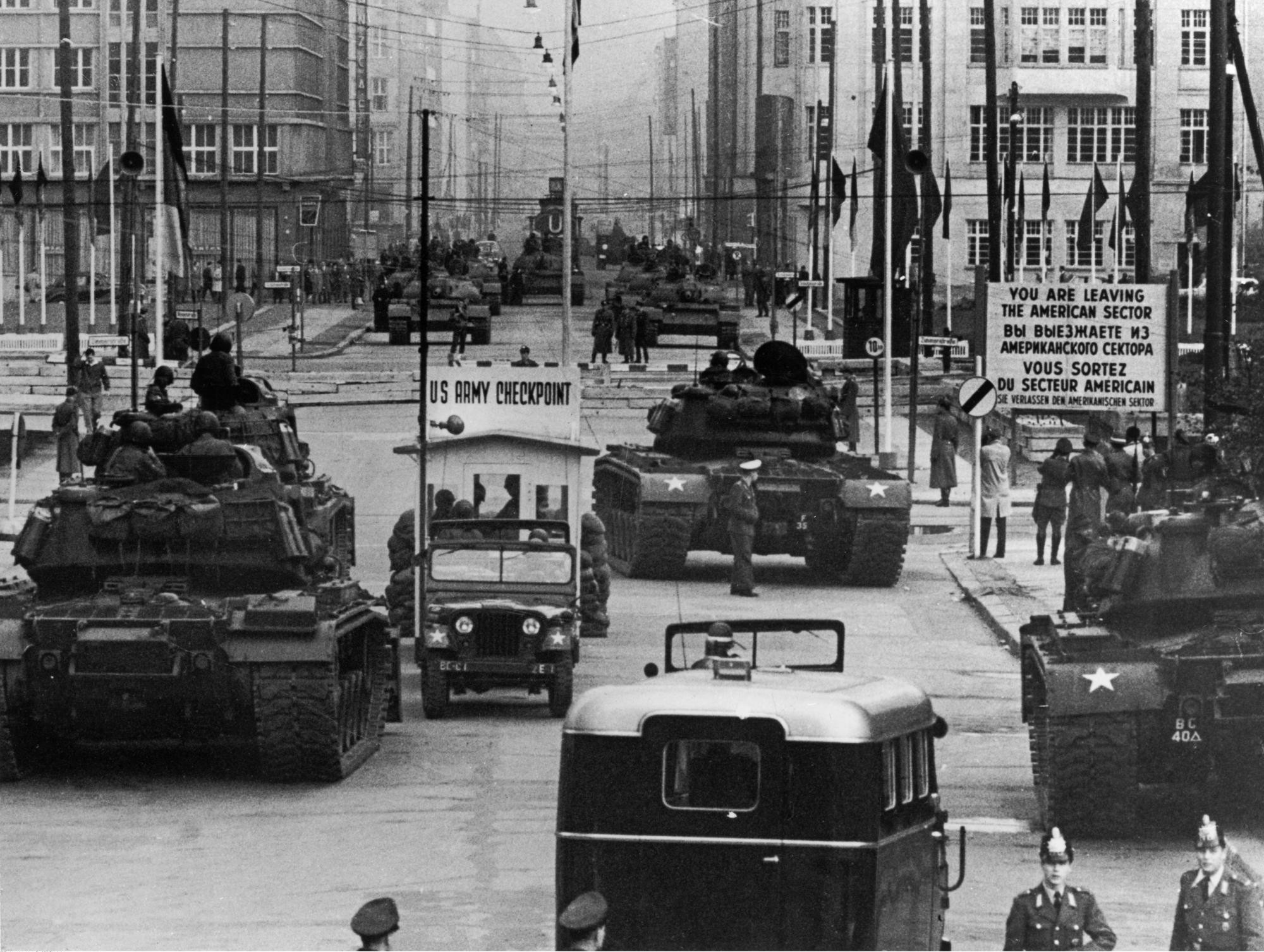  During the Cold War, U.S. troops and their allies fought
During the Cold War, U.S. troops and their allies fought
 During the 1960s, the Department of Defense continued to scrutinize the reserve forces and to question the number of divisions and brigades as well as the redundancy of maintaining two reserve components, the
During the 1960s, the Department of Defense continued to scrutinize the reserve forces and to question the number of divisions and brigades as well as the redundancy of maintaining two reserve components, the
 The Total Force Policy was adopted by Chief of Staff of the Army General Creighton Abrams in the aftermath of the Vietnam War and involved treating the three components of the army – the Regular Army, the
The Total Force Policy was adopted by Chief of Staff of the Army General Creighton Abrams in the aftermath of the Vietnam War and involved treating the three components of the army – the Regular Army, the
 In 1990, Iraq invaded its smaller neighbor, Kuwait, and U.S. land forces quickly deployed to assure the protection of Saudi Arabia. In January 1991 Operation Desert Storm commenced, a U.S.-led coalition which deployed over 500,000 troops, the bulk of them from U.S. Army formations, to drive out Iraqi forces. The campaign ended in total victory, as Western coalition forces routed the
In 1990, Iraq invaded its smaller neighbor, Kuwait, and U.S. land forces quickly deployed to assure the protection of Saudi Arabia. In January 1991 Operation Desert Storm commenced, a U.S.-led coalition which deployed over 500,000 troops, the bulk of them from U.S. Army formations, to drive out Iraqi forces. The campaign ended in total victory, as Western coalition forces routed the  After Operation Desert Storm, the army did not see major combat operations for the remainder of the 1990s but did participate in a number of peacekeeping activities. In 1990 the Department of Defense issued guidance for "rebalancing" after a review of the Total Force Policy, but in 2004, USAF Air War College scholars concluded the guidance would reverse the Total Force Policy which is an "essential ingredient to the successful application of military force".
After Operation Desert Storm, the army did not see major combat operations for the remainder of the 1990s but did participate in a number of peacekeeping activities. In 1990 the Department of Defense issued guidance for "rebalancing" after a review of the Total Force Policy, but in 2004, USAF Air War College scholars concluded the guidance would reverse the Total Force Policy which is an "essential ingredient to the successful application of military force".
 On 11 September 2001, 53 Army civilians (47 employees and six contractors) and 22 soldiers were among the 125 victims killed in the Pentagon in a terrorist attack when
On 11 September 2001, 53 Army civilians (47 employees and six contractors) and 22 soldiers were among the 125 victims killed in the Pentagon in a terrorist attack when  Until 2009, the army's chief modernization plan, its most ambitious since World War II, was the Future Combat Systems program. In 2009, many systems were canceled, and the remaining were swept into the BCT modernization program. By 2017, the Brigade Modernization project was completed and its headquarters, the Brigade Modernization Command, was renamed the Joint Modernization Command, or JMC. In response to Budget sequestration in 2013, Army plans were to shrink to 1940 levels, although actual Active-Army end-strengths were projected to fall to some 450,000 troops by the end of FY2017.Joe Lacdan, Army News Service (March 13, 2019) Soldier pay, quality of life, modernization among priorities in budget proposal
Until 2009, the army's chief modernization plan, its most ambitious since World War II, was the Future Combat Systems program. In 2009, many systems were canceled, and the remaining were swept into the BCT modernization program. By 2017, the Brigade Modernization project was completed and its headquarters, the Brigade Modernization Command, was renamed the Joint Modernization Command, or JMC. In response to Budget sequestration in 2013, Army plans were to shrink to 1940 levels, although actual Active-Army end-strengths were projected to fall to some 450,000 troops by the end of FY2017.Joe Lacdan, Army News Service (March 13, 2019) Soldier pay, quality of life, modernization among priorities in budget proposal
Requested troop strengths: Active (480,000), NG (336,000), and Reserve (189,500) for 2020 budget From 2016 to 2017, the Army retired hundreds of OH-58 Kiowa Warrior observation helicopters, while retaining its Apache gunships. The 2015 expenditure for Army research, development and acquisition changed from $32 billion projected in 2012 for FY15 to $21 billion for FY15 expected in 2014.Drwiega, Andrew.
Missions Solutions Summit: Army Leaders Warn of Rough Ride Ahead
" ''Rotor&Wing'', 4 June 2014. Accessed: 8 June 2014.

References Decker-Wagner 2011 which triggered shifts of units: RDECOM, and ARCIC, from within Army Materiel Command (AMC), and TRADOC, respectively, to a new Army Command (ACOM) in 2018.Secretary of the Army, Mark T. Esper (4 June 2018), ESTABLISHMENT OF UNITED STATES ARMY FUTURES COMMAN
Army General order G.O.2018-10
/ref> The Army Futures Command (AFC), is a peer of FORSCOM, TRADOC, and AMC, the other ACOMs.Source
Organization, United States Army. For detail, see AR10-87
/ref> AFC's mission is modernization reform: to design hardware, as well as to work within the acquisition process which defines materiel for AMC. TRADOC's mission is to define the architecture and organization of the Army, and to train and supply soldiers to FORSCOM. AFC's cross-functional teams (CFTs) are Futures Command's vehicle for sustainable reform of the acquisition process for the future. In order to support the Army's modernization priorities, its FY2020 budget allocated $30 billion for the top six modernization priorities over the next five years. The $30 billion came from $8 billion in cost avoidance and $22 billion in terminations.
 The task of organizing the U.S. Army commenced in 1775. In the first one hundred years of its existence, the United States Army was maintained as a small peacetime force to man permanent
The task of organizing the U.S. Army commenced in 1775. In the first one hundred years of its existence, the United States Army was maintained as a small peacetime force to man permanent  By the twentieth century, the U.S. Army had mobilized the U.S. Volunteers on four occasions during each of the major wars of the nineteenth century. During World War I, the " National Army" was organized to fight the conflict, replacing the concept of U.S. Volunteers. It was demobilized at the end of World War I, and was replaced by the Regular Army, the Organized Reserve Corps and the state militias. In the 1920s and 1930s, the "career" soldiers were known as the " Regular Army" with the "Enlisted Reserve Corps" and "Officer Reserve Corps" augmented to fill vacancies when needed.
In 1941, the " Army of the United States" was founded to fight World War II. The Regular Army, Army of the United States, the National Guard and Officer/Enlisted Reserve Corps (ORC and ERC) existed simultaneously. After World War II, the ORC and ERC were combined into the United States Army Reserve. The Army of the United States was re-established for the Korean War and Vietnam War and was demobilized upon the suspension of the draft.
Currently, the Army is divided into the Regular Army, the Army Reserve and the
By the twentieth century, the U.S. Army had mobilized the U.S. Volunteers on four occasions during each of the major wars of the nineteenth century. During World War I, the " National Army" was organized to fight the conflict, replacing the concept of U.S. Volunteers. It was demobilized at the end of World War I, and was replaced by the Regular Army, the Organized Reserve Corps and the state militias. In the 1920s and 1930s, the "career" soldiers were known as the " Regular Army" with the "Enlisted Reserve Corps" and "Officer Reserve Corps" augmented to fill vacancies when needed.
In 1941, the " Army of the United States" was founded to fight World War II. The Regular Army, Army of the United States, the National Guard and Officer/Enlisted Reserve Corps (ORC and ERC) existed simultaneously. After World War II, the ORC and ERC were combined into the United States Army Reserve. The Army of the United States was re-established for the Korean War and Vietnam War and was demobilized upon the suspension of the draft.
Currently, the Army is divided into the Regular Army, the Army Reserve and the
 Headquarters, United States Department of the Army (HQDA):
Source: U.S. Army organization
Headquarters, United States Department of the Army (HQDA):
Source: U.S. Army organization
 The U.S. Army is made up of three components: the active component, the Regular Army; and two reserve components, the Army National Guard and the Army Reserve. Both reserve components are primarily composed of part-time soldiers who train once a month – known as battle assemblies or unit training assemblies (UTAs) – and conduct two to three weeks of annual training each year. Both the Regular Army and the Army Reserve are organized under Title 10 of the United States Code, while the National Guard is organized under Title 32. While the Army National Guard is organized, trained and equipped as a component of the U.S. Army, when it is not in federal service it is under the command of individual state and territorial governors. However, the District of Columbia National Guard reports to the U.S. president, not the district's mayor, even when not federalized. Any or all of the National Guard can be federalized by presidential order and against the governor's wishes.
The U.S. Army is made up of three components: the active component, the Regular Army; and two reserve components, the Army National Guard and the Army Reserve. Both reserve components are primarily composed of part-time soldiers who train once a month – known as battle assemblies or unit training assemblies (UTAs) – and conduct two to three weeks of annual training each year. Both the Regular Army and the Army Reserve are organized under Title 10 of the United States Code, while the National Guard is organized under Title 32. While the Army National Guard is organized, trained and equipped as a component of the U.S. Army, when it is not in federal service it is under the command of individual state and territorial governors. However, the District of Columbia National Guard reports to the U.S. president, not the district's mayor, even when not federalized. Any or all of the National Guard can be federalized by presidential order and against the governor's wishes.
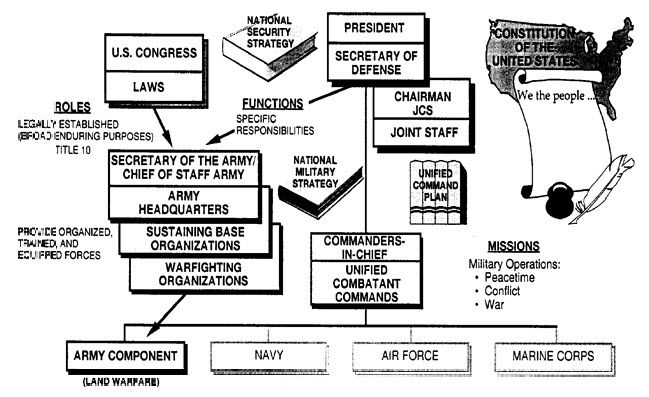
 The U.S. Army is led by a civilian
The U.S. Army is led by a civilian  By 2013, the army shifted to six geographical commands that align with the six geographical unified combatant commands (CCMD):
* United States Army Central headquartered at Shaw Air Force Base, South Carolina
* United States Army North headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas
* United States Army South headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas
* United States Army Europe and Africa headquartered at Clay Kaserne, Wiesbaden, Germany
* United States Army Pacific headquartered at Fort Shafter, Hawaii
By 2013, the army shifted to six geographical commands that align with the six geographical unified combatant commands (CCMD):
* United States Army Central headquartered at Shaw Air Force Base, South Carolina
* United States Army North headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas
* United States Army South headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas
* United States Army Europe and Africa headquartered at Clay Kaserne, Wiesbaden, Germany
* United States Army Pacific headquartered at Fort Shafter, Hawaii
 The army also transformed its base unit from divisions to brigades. Division lineage will be retained, but the divisional headquarters will be able to command any brigade, not just brigades that carry their divisional lineage. The central part of this plan is that each brigade will be modular, i.e., all brigades of the same type will be exactly the same and thus any brigade can be commanded by any division. As specified before the 2013 end-strength re-definitions, the three major types of brigade combat teams are:
* Armored brigades, with a strength of 4,743 troops as of 2014.
* Stryker brigades, with a strength of 4,500 troops as of 2014.
* Infantry brigades, with a strength of 4,413 troops as of 2014.
In addition, there are combat support and service support modular brigades. Combat support brigades include aviation (CAB) brigades, which will come in heavy and light varieties, fires (artillery) brigades (now transforms to division artillery) and expeditionary military intelligence brigades.
The army also transformed its base unit from divisions to brigades. Division lineage will be retained, but the divisional headquarters will be able to command any brigade, not just brigades that carry their divisional lineage. The central part of this plan is that each brigade will be modular, i.e., all brigades of the same type will be exactly the same and thus any brigade can be commanded by any division. As specified before the 2013 end-strength re-definitions, the three major types of brigade combat teams are:
* Armored brigades, with a strength of 4,743 troops as of 2014.
* Stryker brigades, with a strength of 4,500 troops as of 2014.
* Infantry brigades, with a strength of 4,413 troops as of 2014.
In addition, there are combat support and service support modular brigades. Combat support brigades include aviation (CAB) brigades, which will come in heavy and light varieties, fires (artillery) brigades (now transforms to division artillery) and expeditionary military intelligence brigades.
 United States Army Forces Command (FORSCOM)
''For a description of U.S. Army tactical organizational structure, see: a U.S. context and also a global context.''
United States Army Forces Command (FORSCOM)
''For a description of U.S. Army tactical organizational structure, see: a U.S. context and also a global context.''
 United States Army Special Operations Command (Airborne) (USASOC):Army Special Operations Forces Fact Book 2018
United States Army Special Operations Command (Airborne) (USASOC):Army Special Operations Forces Fact Book 2018
, USASOC official website, dated 2018, last accessed 28 July 2019
an
unifies unit and location information for all Soldiers
using Army Organization Server data interface (AOSDI), unified with IPPS-A on the back-end. This allows aggregation of data on ACOM/ASCC, Corps, Division, Brigade, Battalion, Company, Platoon, and Squad levels It will be used for future promotions and other personnel decisions. Among the changes are: * BCAP, the Battalion Commander Assessment Program. In January 2020, over 800 majors and lieutenant colonels from all over the Army converged on Fort Knox to take part in a five-day program to select the next battalion commanders for the Army (beginning in FY2021). This process replaces the former selection process which was based solely on rank and individual reviews of past performance. From now on, more consideration will be given to an individual officer's personal preference, as part of 25 other selection criteria. "Promotion boards will now be able to see almost all substantiated adverse information". The promotion boards will be able to see anything in an officer's human resource record. Officers are encouraged to become familiar with their human resource record, and to file rebuttals to adverse information. * Depending on the success of this initiative, other assessment programs could be instituted as well, for promotion to sergeants major, and for assessment of colonels for command. Below are the U.S. Army ranks authorized for use today and their equivalent NATO designations. Although no living officer currently holds the rank of General of the Army, it is still authorized by Congress for use in wartime.
Future Soldiers
Web Site. including the United States Military Academy, Reserve Officers' Training Corps, Officer Candidate School, and direct commissioning. Regardless of which road an officer takes, the insignia are the same. Certain professions including physicians, pharmacists, nurses, lawyers and chaplains are commissioned directly into the Army. Most army commissioned officers (those who are generalists)Sydney J. Freedberg Jr. (25 October 2017) Can The Pentagon Protect Young Innovators?
Fixing the 'up or out' culture, which favors generalists are promoted based on an "up or out" system. A more flexible talent management process is underway. The Defense Officer Personnel Management Act of 1980 establishes rules for the timing of promotions and limits the number of officers that can serve at any given time. Army regulations call for addressing all personnel with the rank of general as "General (last name)" regardless of the number of stars. Likewise, both colonels and lieutenant colonels are addressed as "Colonel (last name)" and first and second lieutenants as "Lieutenant (last name)".
Enlisted Soldiers Descriptions
Web Site. This distinguishes corporals from the more numerous specialists who have the same pay grade but do not exercise leadership responsibilities. Beginning in 2021, all corporals will be required to conduct
 Training in the U.S. Army is generally divided into two categories – individual and collective. Because of COVID-19 precautions, the first two weeks of basic training — not including processing and out-processing – incorporate social distancing and indoor desk-oriented training. Once the recruits have tested negative for COVID-19 for two weeks, the remaining 8 weeks follow the traditional activities for most recruits, followed by Advanced Individualized Training (AIT) where they receive training for their military occupational specialties (MOS). Some individual's MOSs range anywhere from 14 to 20 weeks of One Station Unit Training (OSUT), which combines Basic Training and AIT. The length of AIT school varies by the MOS. The length of time spent in AIT depends on the MOS of the soldier. Certain highly technical MOS training requires many months (e.g., foreign language translators). Depending on the needs of the army,
Training in the U.S. Army is generally divided into two categories – individual and collective. Because of COVID-19 precautions, the first two weeks of basic training — not including processing and out-processing – incorporate social distancing and indoor desk-oriented training. Once the recruits have tested negative for COVID-19 for two weeks, the remaining 8 weeks follow the traditional activities for most recruits, followed by Advanced Individualized Training (AIT) where they receive training for their military occupational specialties (MOS). Some individual's MOSs range anywhere from 14 to 20 weeks of One Station Unit Training (OSUT), which combines Basic Training and AIT. The length of AIT school varies by the MOS. The length of time spent in AIT depends on the MOS of the soldier. Certain highly technical MOS training requires many months (e.g., foreign language translators). Depending on the needs of the army,  The United States Army Combat Fitness Test (ACFT) was introduced in 2018 to 60 battalions spread throughout the Army. The test and scoring system is the same for all soldiers, regardless of gender. It takes an hour to complete, including resting periods. The ACFT supersedes the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT),Joe Lacdan, Army News Service (22 May 2020) SMA expects ACFT to continue as planned in COVID-19 environment
The United States Army Combat Fitness Test (ACFT) was introduced in 2018 to 60 battalions spread throughout the Army. The test and scoring system is the same for all soldiers, regardless of gender. It takes an hour to complete, including resting periods. The ACFT supersedes the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT),Joe Lacdan, Army News Service (22 May 2020) SMA expects ACFT to continue as planned in COVID-19 environment
"Soldiers can use their last APFT score to remain promotion eligible." as being more relevant to survival in combat. Six events were determined to better predict which muscle groups of the body were adequately conditioned for combat actions: three deadlifts, a standing power throw of a ten-pound medicine ball, hand-release pushups (which replace the traditional pushup), a sprint/drag/carry 250 yard event, three pull-ups with leg tucks (or a plank test in lieu of the leg tuck), a mandatory rest period, and a two-mile run. As of 1 October 2020 all soldiers from all three components (Regular Army, Reserve, and National Guard) are subject to this test. The ACFT now tests all soldiers in basic training as of October 2020. The ACFT became the official test of record 1 October 2020; before that day every Army unit was required to complete a diagnostic ACFTMaj. Stephen Martin (December 27, 2019) Kentucky Guard first to receive ACFT equipment
"36,608 ACFT sets for the total army by May 15". "The Army is focused on the tactical athlete".
Staff Sgt. Warren Wright (10 January 2020) NY National Guard finds creative ways to train for new fitness test
"finding creative ways to exercise at home and on their own time" (All Soldiers with valid APFT scores can use them until March 2022. The Holistic Health and Fitness (H2F) System is one way that soldiers can prepare.).US Army (2020) US Army soldier prepares for ACFT
Learning how to retrain an injured body; using resistance bands (good for leg tucks); know your limits; use out-training (see video for sample); practice technique (good for deadlift, and power throw)Haley Britzk
(27 Oct 2021) This is the Army's plan to stop physically breaking so many of its soldiers
Sexual Harassment/Assault Response & Prevention (SHARP) office is located in Falcon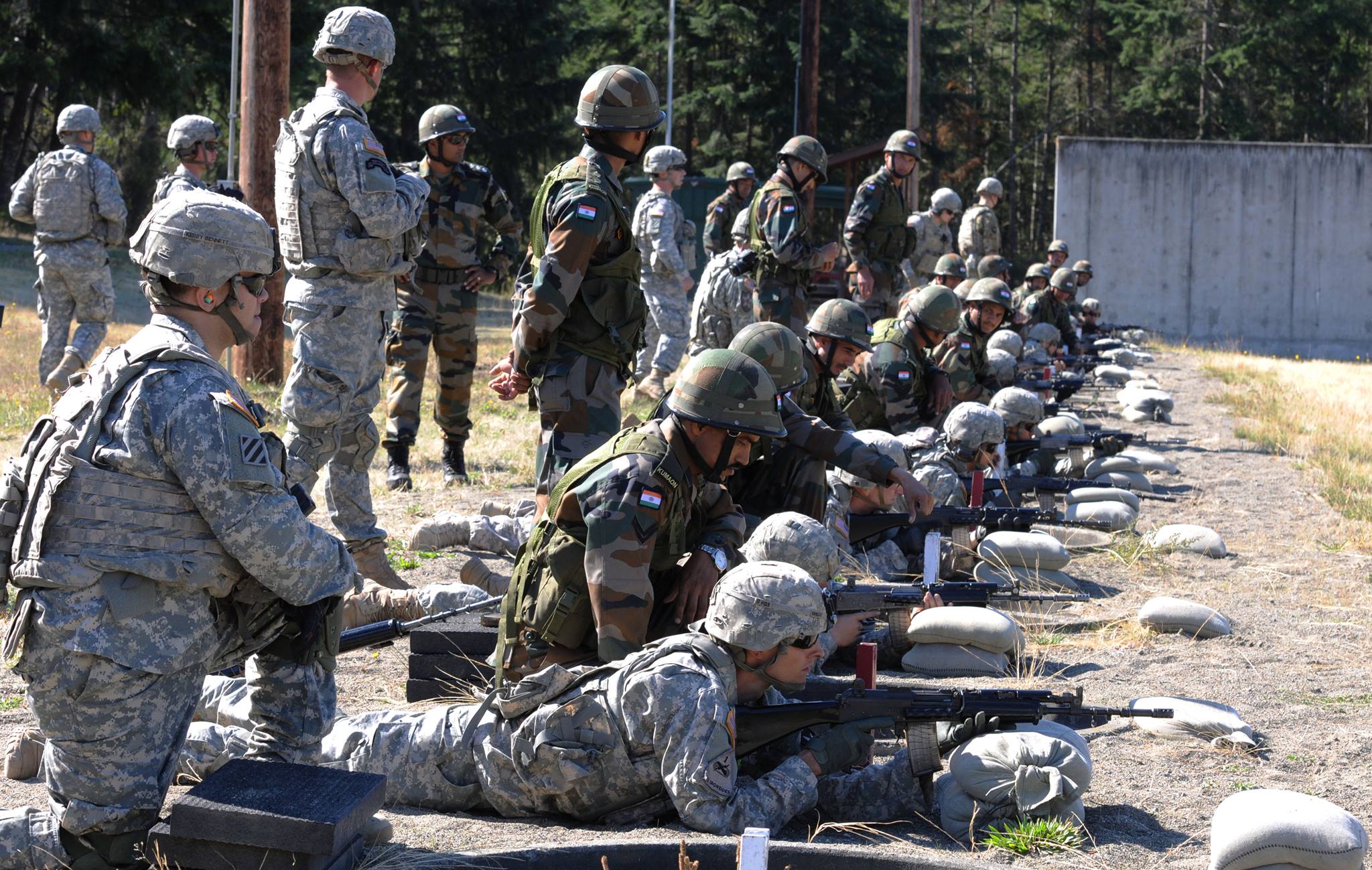 Collective training at the unit level takes place at the unit's assigned station, but the most intensive training at higher echelons is conducted at the three combat training centers (CTC); the National Training Center (NTC) at Fort Irwin, California, the Joint Readiness Training Center (JRTC) at Fort Polk, Louisiana and the
Collective training at the unit level takes place at the unit's assigned station, but the most intensive training at higher echelons is conducted at the three combat training centers (CTC); the National Training Center (NTC) at Fort Irwin, California, the Joint Readiness Training Center (JRTC) at Fort Polk, Louisiana and the
Page 32 lists how this handbook is organized. 440 pages.
 U.S. Army doctrine puts a premium on mechanized warfare. It fields the highest vehicle-to-soldier ratio in the world as of 2009. The army's most common vehicle is the High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV), commonly called the Humvee, which is capable of serving as a cargo/troop carrier, weapons platform and ambulance, among many other roles. While they operate a wide variety of combat support vehicles, one of the most common types centers on the family of HEMTT vehicles. The M1A2 Abrams is the army's main battle tank, while the
U.S. Army doctrine puts a premium on mechanized warfare. It fields the highest vehicle-to-soldier ratio in the world as of 2009. The army's most common vehicle is the High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV), commonly called the Humvee, which is capable of serving as a cargo/troop carrier, weapons platform and ambulance, among many other roles. While they operate a wide variety of combat support vehicles, one of the most common types centers on the family of HEMTT vehicles. The M1A2 Abrams is the army's main battle tank, while the  The U.S. Army's principal artillery weapons are the
The U.S. Army's principal artillery weapons are the
 The Army Combat Uniform (ACU) currently features a camouflage pattern known as Operational Camouflage Pattern (OCP); OCP replaced a pixel-based pattern known as Universal Camouflage Pattern (UCP) in 2019.
The Army Combat Uniform (ACU) currently features a camouflage pattern known as Operational Camouflage Pattern (OCP); OCP replaced a pixel-based pattern known as Universal Camouflage Pattern (UCP) in 2019.
 On 11 November 2018, the Army announced a new version of 'Army Greens' based on uniforms worn during World War II that will become the standard garrison service uniform. The blue Army Service Uniform will remain as the dress uniform. The Army Greens are projected to be first fielded in the summer of 2020.
On 11 November 2018, the Army announced a new version of 'Army Greens' based on uniforms worn during World War II that will become the standard garrison service uniform. The blue Army Service Uniform will remain as the dress uniform. The Army Greens are projected to be first fielded in the summer of 2020.
 The beret flash of enlisted personnel displays their
The beret flash of enlisted personnel displays their
Joe Lacdan (August 13, 2018) Automated meal entitlement system, food trucks to improve Soldier dining experience
Accomplishes paperwork reduction based on reading each soldier's Common Access Card at each use at DFAC. forward operating bases (FOBs), after-action review (AAR), tactical operations center (TOC), morale, welfare and recreation (MWR) facilities, as well as security checkpoints. Furthermore, most of these tents are set up and operated through the support of
United Press International
online review
Army.mil/photos
– United States Army featured photos
U.S. Army Collection
– Missouri History Museum
(compiled by the United States Army Center of Military History)
US-militaria.com
– The U.S. Army during the Second World War {{DEFAULTSORT:United States Army Uniformed services of the United States Military units and formations established in 1775 1775 establishments in the Thirteen Colonies United States Armed Forces service branches
U.S. uniformed services
The United States has eight federal uniformed services that commission officers as defined by Title 10 and subsequently structured and organized by Titles 10, 14, 32, 33 and 42 of the U.S. Code.
Uniformed services
The uniformed services ...
, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the Supremacy Clause, supreme law of the United States, United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven ar ...
(1789). See als
Title 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001
The oldest and most senior branch of the U.S. military in order of precedence, the modern U.S. Army has its roots in the
Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
, which was formed 14 June 1775 to fight the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)—before the United States was established as a country. After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation
The Congress of the Confederation, or the Confederation Congress, formally referred to as the United States in Congress Assembled, was the governing body of the United States of America during the Confederation period, March 1, 1781 – Mar ...
created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army.Library of CongressJournals of the Continental Congress, Volume 27
/ref> The United States Army considers itself to be a continuation of the Continental Army, and thus considers its institutional inception to be the origin of that armed force in 1775. an excerpt from Robert Wright, ''The Continental Army'' The U.S. Army is a uniformed service of the United States and is part of the
Department of the Army
The United States Department of the Army (DA) is one of the three military departments within the Department of Defense of the U.S. The Department of the Army is the federal government agency within which the United States Army (U.S.) is org ...
, which is one of the three military departments of the Department of Defense. The U.S. Army is headed by a civilian senior appointed civil servant, the secretary of the Army
The secretary of the Army (SA or SECARMY) is a senior civilian official within the United States Department of Defense, with statutory responsibility for all matters relating to the United States Army: manpower, personnel, reserve affairs, insta ...
(SECARMY) and by a chief military officer
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.
Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer, or a warrant officer. However, absent context ...
, the chief of staff of the Army (CSA) who is also a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. It is the largest military branch, and in the fiscal year 2020, the projected end strength for the Regular Army (USA) was 480,893 soldiers; the Army National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG), in conjunction with the Air National Guard, is an organized Militia (United States), militia force and a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States A ...
(ARNG) had 336,129 soldiers and the U.S. Army Reserve (USAR) had 188,703 soldiers; the combined-component strength of the U.S. Army was 1,005,725 soldiers. As a branch of the armed forces, the mission of the U.S. Army is "to fight and win our Nation's wars, by providing prompt, sustained land dominance, across the full range of military operations and the spectrum of conflict, in support of combatant commanders". The branch participates in conflicts worldwide and is the major ground-based offensive and defensive force of the United States.
Mission
The United States Army serves as the land-based branch of the U.S. Armed ForcesSection 7062 of Title 10, U.S. Code
defines the purpose of the army as: * Preserving the peace and security and providing for the defense of the United States, the Commonwealths and possessions and any areas occupied by the United States * Supporting the national policies * Implementing the national objectives * Overcoming any nations responsible for aggressive acts that imperil the peace and security of the United States In 2018, the ''Army Strategy 2018'' articulated an eight-point addendum to the Army Vision for 2028.The Army Strategy
2018 While the Army Mission remains constant, the Army Strategy builds upon the Army's Brigade Modernization by adding focus to Corps and Division-level echelons.
Modernization
Modernization theory is used to explain the process of modernization within societies. The "classical" theories of modernization of the 1950s and 1960s drew on sociological analyses of Karl Marx, Emile Durkheim and a partial reading of Max Weber, ...
, reform for high-intensity conflict, and Joint multi-domain operations are added to the strategy, to be completed by 2028.
The Army's five core competencies are prompt and sustained land combat, combined arms operations (to include combined arms maneuver and wide–area security, armored and mechanized operations and airborne and air assault operations), special operations, to set and sustain the theater for the joint force, and to integrate national, multinational, and joint power on land.
History
Origins
The Continental Army was created on 14 June 1775 by theSecond Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
as a unified army for the colonies to fight Great Britain, with George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
appointed as its commander. The army was initially led by men who had served in the British Army or colonial militias and who brought much of British military heritage with them. As the Revolutionary War progressed, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
aid, resources and military thinking helped shape the new army. A number of European soldiers came on their own to help, such as Friedrich Wilhelm von Steuben, who taught Prussian Army
The Royal Prussian Army (1701–1919, german: Königlich Preußische Armee) served as the army of the Kingdom of Prussia. It became vital to the development of Brandenburg-Prussia as a European power.
The Prussian Army had its roots in the co ...
tactics and organizational skills.
 The Army fought numerous pitched battles, and sometimes used Fabian strategy and hit-and-run tactics in the South in 1780 and 1781; Under Major General Nathanael Greene, it hit where the British were weakest to wear down their forces. Washington led victories against the British at Trenton and Princeton, but lost a series of battles in the
The Army fought numerous pitched battles, and sometimes used Fabian strategy and hit-and-run tactics in the South in 1780 and 1781; Under Major General Nathanael Greene, it hit where the British were weakest to wear down their forces. Washington led victories against the British at Trenton and Princeton, but lost a series of battles in the New York and New Jersey campaign
The New York and New Jersey campaign in 1776 and the winter months of 1777 was a series of American Revolutionary War battles for control of the Port of New York and New Jersey, Port of New York and the state of New Jersey, fought between Kingdom ...
in 1776 and the Philadelphia campaign in 1777. With a decisive victory at Yorktown and the help of the French, the Continental Army prevailed against the British.
After the war, the Continental Army was quickly given land certificates and disbanded in a reflection of the republican distrust of standing armies. State militias became the new nation's sole ground army, with the exception of a regiment to guard the Western Frontier and one battery of artillery guarding West Point's arsenal. However, because of continuing conflict with Native Americans, it was soon realized that it was necessary to field a trained standing army. The Regular Army was at first very small and after General St. Clair's defeat at the Battle of the Wabash, where more than 800 Americans were killed, the Regular Army was reorganized as the Legion of the United States, which was established in 1791 and renamed the United States Army in 1796.
In 1798, during the Quasi-War with France, Congress established a three-year " Provisional Army" of 10,000 men, consisting of twelve regiments of infantry and six troops of light dragoons. By March 1799 Congress created an "Eventual Army" of 30,000 men, including three regiments of cavalry. Both "armies" existed only on paper, but equipment for 3,000 men and horses was procured and stored.
19th century
Early wars on the Frontier
 The War of 1812, the second and last war between the United States and Great Britain, had mixed results. The U.S. Army did not conquer Canada but it did destroy Native American resistance to expansion in the Old Northwest and it validated its independence by stopping two major British invasions in 1814 and 1815. After taking control of Lake Erie in 1813, the U.S. Army seized parts of western Upper Canada, burned York and defeated Tecumseh, which caused his Western Confederacy to collapse. Following U.S. victories in the Canadian province of Upper Canada, British troops who had dubbed the U.S. Army "Regulars, by God!", were able to capture and burn Washington, which was defended by militia, in 1814. The regular army, however, proved they were professional and capable of defeating the British army during the invasions of Plattsburgh and
The War of 1812, the second and last war between the United States and Great Britain, had mixed results. The U.S. Army did not conquer Canada but it did destroy Native American resistance to expansion in the Old Northwest and it validated its independence by stopping two major British invasions in 1814 and 1815. After taking control of Lake Erie in 1813, the U.S. Army seized parts of western Upper Canada, burned York and defeated Tecumseh, which caused his Western Confederacy to collapse. Following U.S. victories in the Canadian province of Upper Canada, British troops who had dubbed the U.S. Army "Regulars, by God!", were able to capture and burn Washington, which was defended by militia, in 1814. The regular army, however, proved they were professional and capable of defeating the British army during the invasions of Plattsburgh and Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was d ...
, prompting British agreement on the previously rejected terms of a status quo
is a Latin phrase meaning the existing state of affairs, particularly with regard to social, political, religious or military issues. In the sociological sense, the ''status quo'' refers to the current state of social structure and/or values. W ...
antebellum. Two weeks after a treaty was signed (but not ratified), Andrew Jackson defeated the British in the Battle of New Orleans and Siege of Fort St. Philip, and became a national hero. U.S. troops and sailors captured HMS Cyane, Levant and Penguin
Penguins (order (biology), order List of Sphenisciformes by population, Sphenisciformes , family (biology), family Spheniscidae ) are a group of Water bird, aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere: on ...
in the final engagements of the war. Per the treaty, both sides (the United States and Great Britain) returned to the geographical status quo. Both navies kept the warships they had seized during the conflict.
The army's major campaign against the Indians was fought in Florida against Seminoles. It took long wars (1818–1858) to finally defeat the Seminoles and move them to Oklahoma. The usual strategy in Indian wars was to seize control of the Indians' winter food supply, but that was no use in Florida where there was no winter. The second strategy was to form alliances with other Indian tribes, but that too was useless because the Seminoles had destroyed all the other Indians when they entered Florida in the late eighteenth century.
The U.S. Army fought and won the Mexican–American War (1846–1848), which was a defining event for both countries. The U.S. victory resulted in acquisition of territory that eventually became all or parts of the states of California, Nevada, Utah, Colorado, Arizona, Wyoming and New Mexico.
American Civil War
 The American Civil War was the costliest war for the U.S. in terms of casualties. After most slave states, located in the southern U.S., formed the Confederate States, the Confederate States Army, led by former U.S. Army officers, mobilized a large fraction of Southern white manpower. Forces of the United States (the "Union" or "the North") formed the Union Army, consisting of a small body of regular army units and a large body of volunteer units raised from every state, north and south, except South Carolina.
For the first two years, Confederate forces did well in set battles but lost control of the border states. The Confederates had the advantage of defending a large territory in an area where disease caused twice as many deaths as combat. The Union pursued a strategy of seizing the coastline, blockading the ports, and taking control of the river systems. By 1863, the Confederacy was being strangled. Its eastern armies fought well, but the western armies were defeated one after another until the Union forces captured New Orleans in 1862 along with the Tennessee River. In the Vicksburg Campaign of 1862–1863, General Ulysses Grant seized the Mississippi River and cut off the Southwest. Grant took command of Union forces in 1864 and after a series of battles with very heavy casualties, he had General
The American Civil War was the costliest war for the U.S. in terms of casualties. After most slave states, located in the southern U.S., formed the Confederate States, the Confederate States Army, led by former U.S. Army officers, mobilized a large fraction of Southern white manpower. Forces of the United States (the "Union" or "the North") formed the Union Army, consisting of a small body of regular army units and a large body of volunteer units raised from every state, north and south, except South Carolina.
For the first two years, Confederate forces did well in set battles but lost control of the border states. The Confederates had the advantage of defending a large territory in an area where disease caused twice as many deaths as combat. The Union pursued a strategy of seizing the coastline, blockading the ports, and taking control of the river systems. By 1863, the Confederacy was being strangled. Its eastern armies fought well, but the western armies were defeated one after another until the Union forces captured New Orleans in 1862 along with the Tennessee River. In the Vicksburg Campaign of 1862–1863, General Ulysses Grant seized the Mississippi River and cut off the Southwest. Grant took command of Union forces in 1864 and after a series of battles with very heavy casualties, he had General Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nort ...
under siege in Richmond as General William T. Sherman captured Atlanta and marched through Georgia and the Carolinas. The Confederate capital was abandoned in April 1865 and Lee subsequently surrendered his army at Appomattox Court House. All other Confederate armies surrendered within a few months.
The war remains the deadliest conflict in U.S. history, resulting in the deaths of 620,000 men on both sides. Based on 1860 census figures, 8% of all white males aged 13 to 43 died in the war, including 6.4% in the North and 18% in the South.
Later 19th century
 Following the Civil War, the U.S. Army had the mission of containing western tribes of Native Americans on the
Following the Civil War, the U.S. Army had the mission of containing western tribes of Native Americans on the Indian reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which it ...
s. They set up many forts, and engaged in the last of the American Indian Wars. U.S. Army troops also occupied several Southern states during the Reconstruction Era
The Reconstruction era was a period in American history following the American Civil War (1861–1865) and lasting until approximately the Compromise of 1877. During Reconstruction, attempts were made to rebuild the country after the bloo ...
to protect freedmen.
The key battles of the Spanish–American War of 1898 were fought by the Navy. Using mostly new volunteers, the U.S. forces defeated Spain in land campaigns in Cuba and played the central role in the Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War or Filipino–American War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang Pilipino–Amerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
.
20th century
Starting in 1910, the army began acquiringfixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinc ...
. In 1910, during the Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution ( es, Revolución Mexicana) was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from approximately 1910 to 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It resulted in the destruction ...
, the army was deployed to U.S. towns near the border to ensure the safety of lives and property. In 1916, Pancho Villa, a major rebel leader, attacked Columbus, New Mexico, prompting a U.S. intervention in Mexico until 7 February 1917. They fought the rebels and the Mexican federal troops until 1918.
World wars
 The United States joined World War I as an "Associated Power" in 1917 on the side of Britain, France, Russia, Italy and the other Allies. U.S. troops were sent to the
The United States joined World War I as an "Associated Power" in 1917 on the side of Britain, France, Russia, Italy and the other Allies. U.S. troops were sent to the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
*Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a majo ...
and were involved in the last offensives that ended the war. With the armistice in November 1918, the army once again decreased its forces.
In 1939, estimates of the Army's strength range between 174,000 and 200,000 soldiers, smaller than that of Portugal's, which ranked it 17th or 19th in the world in size. General George C. Marshall became Army chief of staff in September 1939 and set about expanding and modernizing the Army in preparation for war.
 The United States joined World War II in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. Some 11 million Americans were to serve in various Army operations.. Other sources count the Army of Occupation up to 31 December 1946. By 30 June 1947 the Army's strength was down to 990,000 troops. On the European front, U.S. Army troops formed a significant portion of the forces that landed in French North Africa and took Tunisia and then moved on to Sicily and later fought in Italy. In the June 1944 landings in northern France and in the subsequent
The United States joined World War II in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. Some 11 million Americans were to serve in various Army operations.. Other sources count the Army of Occupation up to 31 December 1946. By 30 June 1947 the Army's strength was down to 990,000 troops. On the European front, U.S. Army troops formed a significant portion of the forces that landed in French North Africa and took Tunisia and then moved on to Sicily and later fought in Italy. In the June 1944 landings in northern France and in the subsequent liberation of Europe
The final battle of the European Theatre of World War II continued after the definitive overall surrender of Nazi Germany to the Allies, signed by Field marshal Wilhelm Keitel on 8 May 1945 in Karlshorst, Berlin. After German dictator Ad ...
and defeat of Nazi Germany, millions of U.S. Army troops played a central role. In 1947, the number of soldiers in the US Army had decreased from eight million in 1945 to 684,000 soldiers and the total number of active divisions had dropped from 89 to 12. The leaders of the Army saw this demobilization as a success.
In the Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast ...
, U.S. Army soldiers participated alongside the United States Marine Corps in capturing the Pacific Islands
Collectively called the Pacific Islands, the islands in the Pacific Ocean are further categorized into three major island groups: Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Depending on the context, the term ''Pacific Islands'' may refer to one of se ...
from Japanese control. Following the Axis surrenders in May (Germany) and August (Japan) of 1945, army troops were deployed to Japan and Germany to occupy the two defeated nations. Two years after World War II, the Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
separated from the army to become the United States Air Force in September 1947. In 1948, the army was desegregated by order 9981 of President Harry S. Truman.
Cold War
=1945–1960
= The end of World War II set the stage for the East–West confrontation known as the
The end of World War II set the stage for the East–West confrontation known as the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
. With the outbreak of the Korean War, concerns over the defense of Western Europe rose. Two corps, V and VII, were reactivated under Seventh United States Army
The Seventh Army was a United States army created during World War II that evolved into the United States Army Europe (USAREUR) during the 1950s and 1960s. It served in North Africa and Italy in the Mediterranean Theater of Operations and Fran ...
in 1950 and U.S. strength in Europe rose from one division to four. Hundreds of thousands of U.S. troops remained stationed in West Germany, with others in Belgium, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, until the 1990s in anticipation of a possible Soviet attack.
 During the Cold War, U.S. troops and their allies fought
During the Cold War, U.S. troops and their allies fought communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
forces in Korea and Vietnam. The Korean War began in June 1950, when the Soviets walked out of a UN Security Council meeting, removing their possible veto. Under a United Nations umbrella, hundreds of thousands of U.S. troops fought to prevent the takeover of South Korea by North Korea and later to invade the northern nation. After repeated advances and retreats by both sides and the Chinese People's Volunteer Army
The People's Volunteer Army (PVA) was the armed expeditionary forces deployed by the People's Republic of China during the Korean War. Although all units in the PVA were actually transferred from the People's Liberation Army under the order ...
's entry into the war, the Korean Armistice Agreement returned the peninsula to the status quo in July 1953.
=1960–1970
= The Vietnam War is often regarded as a low point for the U.S. Army due to the use of drafted personnel, the unpopularity of the war with the U.S. public and frustrating restrictions placed on the military by U.S. political leaders. While U.S. forces had been stationed inSouth Vietnam
South Vietnam, officially the Republic of Vietnam ( vi, Việt Nam Cộng hòa), was a state in Southeast Asia that existed from 1955 to 1975, the period when the southern portion of Vietnam was a member of the Western Bloc during part of th ...
since 1959, in intelligence and advising/training roles, they were not deployed in large numbers until 1965, after the Gulf of Tonkin Incident
The Gulf of Tonkin incident ( vi, Sự kiện Vịnh Bắc Bộ) was an international confrontation that led to the United States engaging more directly in the Vietnam War. It involved both a proven confrontation on August 2, 1964, carried out b ...
. U.S. forces effectively established and maintained control of the "traditional" battlefield, but they struggled to counter the guerrilla hit and run tactics of the communist Viet Cong and the People's Army Of Vietnam (NVA).
 During the 1960s, the Department of Defense continued to scrutinize the reserve forces and to question the number of divisions and brigades as well as the redundancy of maintaining two reserve components, the
During the 1960s, the Department of Defense continued to scrutinize the reserve forces and to question the number of divisions and brigades as well as the redundancy of maintaining two reserve components, the Army National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG), in conjunction with the Air National Guard, is an organized Militia (United States), militia force and a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States A ...
and the Army Reserve. In 1967, Secretary of Defense Robert McNamara decided that 15 combat divisions in the Army National Guard were unnecessary and cut the number to eight divisions (one mechanized infantry, two armored, and five infantry), but increased the number of brigades from seven to 18 (one airborne, one armored, two mechanized infantry and 14 infantry). The loss of the divisions did not sit well with the states. Their objections included the inadequate maneuver element mix for those that remained and the end to the practice of rotating divisional commands among the states that supported them. Under the proposal, the remaining division commanders were to reside in the state of the division base. However, no reduction in total Army National Guard strength was to take place, which convinced the governors to accept the plan. The states reorganized their forces accordingly between 1 December 1967 and 1 May 1968.
=1970–1990
= The Total Force Policy was adopted by Chief of Staff of the Army General Creighton Abrams in the aftermath of the Vietnam War and involved treating the three components of the army – the Regular Army, the
The Total Force Policy was adopted by Chief of Staff of the Army General Creighton Abrams in the aftermath of the Vietnam War and involved treating the three components of the army – the Regular Army, the Army National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG), in conjunction with the Air National Guard, is an organized Militia (United States), militia force and a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States A ...
and the Army Reserve as a single force. General Abrams' intertwining of the three components of the army effectively made extended operations impossible without the involvement of both the Army National Guard and Army Reserve in a predominantly combat support role. The army converted to an all-volunteer force with greater emphasis on training to specific performance standards driven by the reforms of General William E. DePuy, the first commander of United States Army Training and Doctrine Command. Following the Camp David Accords that was signed by Egypt, Israel that was brokered by president Jimmy Carter in 1978, as part of the agreement, both the United States and Egypt agreed that there would be a joint military training led by both countries that would usually take place every 2 years, that exercise is known as Exercise Bright Star
Exercise Bright Star is a series of combined and joint training exercises led by United States and Egyptian forces in Egypt held every two years. These exercises began in 1980, rooted in the 1977 Camp David Accords. After its signing, the Egy ...
.
The 1980s was mostly a decade of reorganization. The Goldwater-Nichols Act of 1986 created unified combatant commands bringing the army together with the other four military services under unified, geographically organized command structures. The army also played a role in the invasions of Grenada
Grenada ( ; Grenadian Creole French: ) is an island country in the West Indies in the Caribbean Sea at the southern end of the Grenadines island chain. Grenada consists of the island of Grenada itself, two smaller islands, Carriacou and Pe ...
in 1983 (Operation Urgent Fury
The United States invasion of Grenada began at dawn on 25 October 1983. The United States and a coalition of six Caribbean nations invaded the island nation of Grenada, north of Venezuela. Codenamed Operation Urgent Fury by the U.S. military, ...
) and Panama in 1989 ( Operation Just Cause).
By 1989 Germany was nearing reunification and the Cold War was coming to a close. Army leadership reacted by starting to plan for a reduction in strength. By November 1989 Pentagon briefers were laying out plans to reduce army end strength by 23%, from 750,000 to 580,000. A number of incentives such as early retirement were used.
1990s
 In 1990, Iraq invaded its smaller neighbor, Kuwait, and U.S. land forces quickly deployed to assure the protection of Saudi Arabia. In January 1991 Operation Desert Storm commenced, a U.S.-led coalition which deployed over 500,000 troops, the bulk of them from U.S. Army formations, to drive out Iraqi forces. The campaign ended in total victory, as Western coalition forces routed the
In 1990, Iraq invaded its smaller neighbor, Kuwait, and U.S. land forces quickly deployed to assure the protection of Saudi Arabia. In January 1991 Operation Desert Storm commenced, a U.S.-led coalition which deployed over 500,000 troops, the bulk of them from U.S. Army formations, to drive out Iraqi forces. The campaign ended in total victory, as Western coalition forces routed the Iraqi Army
The Iraqi Ground Forces (Arabic: القوات البرية العراقية), or the Iraqi Army (Arabic: الجيش العراقي), is the ground force component of the Iraqi Armed Forces. It was known as the Royal Iraqi Army up until the coup ...
. Some of the largest tank battles in history were fought during the Gulf war. The Battle of Medina Ridge
The Battle of Medina Ridge was a tank battle fought on the 27 February 1991, during the Gulf War, between the U.S. 1st Armored Division and the 2nd Brigade of the Iraqi Republican Guard Medina Luminous Division outside Basra, Iraq. The U.S. 3rd ...
, Battle of Norfolk and the Battle of 73 Easting were tank battles of historical significance.
 After Operation Desert Storm, the army did not see major combat operations for the remainder of the 1990s but did participate in a number of peacekeeping activities. In 1990 the Department of Defense issued guidance for "rebalancing" after a review of the Total Force Policy, but in 2004, USAF Air War College scholars concluded the guidance would reverse the Total Force Policy which is an "essential ingredient to the successful application of military force".
After Operation Desert Storm, the army did not see major combat operations for the remainder of the 1990s but did participate in a number of peacekeeping activities. In 1990 the Department of Defense issued guidance for "rebalancing" after a review of the Total Force Policy, but in 2004, USAF Air War College scholars concluded the guidance would reverse the Total Force Policy which is an "essential ingredient to the successful application of military force".
21st century
 On 11 September 2001, 53 Army civilians (47 employees and six contractors) and 22 soldiers were among the 125 victims killed in the Pentagon in a terrorist attack when
On 11 September 2001, 53 Army civilians (47 employees and six contractors) and 22 soldiers were among the 125 victims killed in the Pentagon in a terrorist attack when American Airlines Flight 77
American Airlines Flight 77 was a scheduled American Airlines domestic transcontinental passenger flight from Washington Dulles International Airport in Dulles, Virginia, to Los Angeles International Airport in Los Angeles, California. The Boe ...
commandeered by five Al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
hijackers slammed into the western side of the building, as part of the September 11 attacks. In response to the 11 September attacks and as part of the Global War on Terror
The war on terror, officially the Global War on Terrorism (GWOT), is an ongoing international counterterrorism military campaign initiated by the United States following the September 11 attacks. The main targets of the campaign are militant I ...
, U.S. and NATO forces invaded Afghanistan in October 2001, displacing the Taliban government. The U.S. Army also led the combined U.S. and allied invasion of Iraq in 2003; it served as the primary source for ground forces with its ability to sustain short and long-term deployment operations. In the following years, the mission changed from conflict between regular militaries to counterinsurgency, resulting in the deaths of more than 4,000 U.S. service members (as of March 2008) and injuries to thousands more. . By Gilbert Burnham, Shannon Doocy, Elizabeth Dzeng, Riyadh Lafta, and Les Roberts. A supplement to the second ''Lancet'' study. 23,813 insurgents were killed in Iraq between 2003 and 2011.
 Until 2009, the army's chief modernization plan, its most ambitious since World War II, was the Future Combat Systems program. In 2009, many systems were canceled, and the remaining were swept into the BCT modernization program. By 2017, the Brigade Modernization project was completed and its headquarters, the Brigade Modernization Command, was renamed the Joint Modernization Command, or JMC. In response to Budget sequestration in 2013, Army plans were to shrink to 1940 levels, although actual Active-Army end-strengths were projected to fall to some 450,000 troops by the end of FY2017.Joe Lacdan, Army News Service (March 13, 2019) Soldier pay, quality of life, modernization among priorities in budget proposal
Until 2009, the army's chief modernization plan, its most ambitious since World War II, was the Future Combat Systems program. In 2009, many systems were canceled, and the remaining were swept into the BCT modernization program. By 2017, the Brigade Modernization project was completed and its headquarters, the Brigade Modernization Command, was renamed the Joint Modernization Command, or JMC. In response to Budget sequestration in 2013, Army plans were to shrink to 1940 levels, although actual Active-Army end-strengths were projected to fall to some 450,000 troops by the end of FY2017.Joe Lacdan, Army News Service (March 13, 2019) Soldier pay, quality of life, modernization among priorities in budget proposalRequested troop strengths: Active (480,000), NG (336,000), and Reserve (189,500) for 2020 budget From 2016 to 2017, the Army retired hundreds of OH-58 Kiowa Warrior observation helicopters, while retaining its Apache gunships. The 2015 expenditure for Army research, development and acquisition changed from $32 billion projected in 2012 for FY15 to $21 billion for FY15 expected in 2014.Drwiega, Andrew.
Missions Solutions Summit: Army Leaders Warn of Rough Ride Ahead
" ''Rotor&Wing'', 4 June 2014. Accessed: 8 June 2014.
Organization
Planning
By 2017, a task force was formed to address Army modernization,Army Directive 2017–33 (Enabling the Army Modernization Task Force) (7 November 2017)References Decker-Wagner 2011 which triggered shifts of units: RDECOM, and ARCIC, from within Army Materiel Command (AMC), and TRADOC, respectively, to a new Army Command (ACOM) in 2018.Secretary of the Army, Mark T. Esper (4 June 2018), ESTABLISHMENT OF UNITED STATES ARMY FUTURES COMMAN
Army General order G.O.2018-10
/ref> The Army Futures Command (AFC), is a peer of FORSCOM, TRADOC, and AMC, the other ACOMs.Source
Organization, United States Army. For detail, see AR10-87
/ref> AFC's mission is modernization reform: to design hardware, as well as to work within the acquisition process which defines materiel for AMC. TRADOC's mission is to define the architecture and organization of the Army, and to train and supply soldiers to FORSCOM. AFC's cross-functional teams (CFTs) are Futures Command's vehicle for sustainable reform of the acquisition process for the future. In order to support the Army's modernization priorities, its FY2020 budget allocated $30 billion for the top six modernization priorities over the next five years. The $30 billion came from $8 billion in cost avoidance and $22 billion in terminations.
Army Components
 The task of organizing the U.S. Army commenced in 1775. In the first one hundred years of its existence, the United States Army was maintained as a small peacetime force to man permanent
The task of organizing the U.S. Army commenced in 1775. In the first one hundred years of its existence, the United States Army was maintained as a small peacetime force to man permanent forts
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
and perform other non-wartime duties such as engineering and construction works. During times of war, the U.S. Army was augmented by the much larger United States Volunteers which were raised independently by various state governments. States also maintained full-time militias which could also be called into the service of the army.
Army National Guard
The Army National Guard (ARNG), in conjunction with the Air National Guard, is an organized Militia (United States), militia force and a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States A ...
. Some states further maintain state defense forces, as a type of reserve to the National Guard, while all states maintain regulations for state militias. State militias are both "organized", meaning that they are armed forces usually part of the state defense forces, or "unorganized" simply meaning that all able-bodied males may be eligible to be called into military service.
The U.S. Army is also divided into several branches and functional areas. Branches include officers, warrant officers, and enlisted Soldiers while functional areas consist of officers who are reclassified from their former branch into a functional area. However, officers continue to wear the branch insignia of their former branch in most cases, as functional areas do not generally have discrete insignia. Some branches, such as Special Forces
Special forces and special operations forces (SOF) are military units trained to conduct special operations. NATO has defined special operations as "military activities conducted by specially designated, organized, selected, trained and equip ...
, operate similarly to functional areas in that individuals may not join their ranks until having served in another Army branch. Careers in the Army can extend into cross-functional areas for officer, warrant officer, enlisted, and civilian personnel.
Before 1933, members of the Army National Guard were considered state militia until they were mobilized into the U.S. Army, typically on the onset of war. Since the 1933 amendment to the National Defense Act of 1916, all Army National Guard soldiers have held dual status. They serve as National Guardsmen under the authority of the governor of their state or territory and as reserve members of the U.S. Army under the authority of the president, in the Army National Guard of the United States.
Since the adoption of the total force policy, in the aftermath of the Vietnam War, reserve component soldiers have taken a more active role in U.S. military operations. For example, Reserve and Guard units took part in the Gulf War, peacekeeping in Kosovo, Afghanistan, and the 2003 invasion of Iraq
The 2003 invasion of Iraq was a United States-led invasion of the Republic of Iraq and the first stage of the Iraq War. The invasion phase began on 19 March 2003 (air) and 20 March 2003 (ground) and lasted just over one month, including 26 ...
.
Army commands and army service component commands
 Headquarters, United States Department of the Army (HQDA):
Source: U.S. Army organization
Headquarters, United States Department of the Army (HQDA):
Source: U.S. Army organization
Structure
SeeStructure of the United States Army
The structure of the United States Army is complex, and can be interpreted in several different ways: active/reserve, operational/administrative, and branches/functional areas.
From time to time the Department of the Army issues Department o ...
for a detailed treatment of the history, components
Circuit Component may refer to:
•Are devices that perform functions when they are connected in a circuit.
In engineering, science, and technology Generic systems
* System components, an entity with discrete structure, such as an assem ...
, administrative and operational structure and the branches and functional areas of the Army.
 The U.S. Army is made up of three components: the active component, the Regular Army; and two reserve components, the Army National Guard and the Army Reserve. Both reserve components are primarily composed of part-time soldiers who train once a month – known as battle assemblies or unit training assemblies (UTAs) – and conduct two to three weeks of annual training each year. Both the Regular Army and the Army Reserve are organized under Title 10 of the United States Code, while the National Guard is organized under Title 32. While the Army National Guard is organized, trained and equipped as a component of the U.S. Army, when it is not in federal service it is under the command of individual state and territorial governors. However, the District of Columbia National Guard reports to the U.S. president, not the district's mayor, even when not federalized. Any or all of the National Guard can be federalized by presidential order and against the governor's wishes.
The U.S. Army is made up of three components: the active component, the Regular Army; and two reserve components, the Army National Guard and the Army Reserve. Both reserve components are primarily composed of part-time soldiers who train once a month – known as battle assemblies or unit training assemblies (UTAs) – and conduct two to three weeks of annual training each year. Both the Regular Army and the Army Reserve are organized under Title 10 of the United States Code, while the National Guard is organized under Title 32. While the Army National Guard is organized, trained and equipped as a component of the U.S. Army, when it is not in federal service it is under the command of individual state and territorial governors. However, the District of Columbia National Guard reports to the U.S. president, not the district's mayor, even when not federalized. Any or all of the National Guard can be federalized by presidential order and against the governor's wishes.
 The U.S. Army is led by a civilian
The U.S. Army is led by a civilian secretary of the Army
The secretary of the Army (SA or SECARMY) is a senior civilian official within the United States Department of Defense, with statutory responsibility for all matters relating to the United States Army: manpower, personnel, reserve affairs, insta ...
, who has the statutory authority to conduct all the affairs of the army under the authority, direction and control of the secretary of defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
. The chief of staff of the Army, who is the highest-ranked military officer in the army, serves as the principal military adviser and executive agent for the secretary of the Army, i.e., its service chief; and as a member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, a body composed of the service chiefs from each of the four military services belonging to the Department of Defense who advise the president of the United States, the secretary of defense and the National Security Council
A national security council (NSC) is usually an executive branch governmental body responsible for coordinating policy on national security issues and advising chief executives on matters related to national security. An NSC is often headed by a na ...
on operational military matters, under the guidance of the chairman
The chairperson, also chairman, chairwoman or chair, is the presiding officer of an organized group such as a board, committee, or deliberative assembly. The person holding the office, who is typically elected or appointed by members of the grou ...
and vice chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. In 1986, the Goldwater–Nichols Act
The Goldwater–Nichols Department of Defense Reorganization Act of October 4, 1986 , (signed by President Ronald Reagan), made the most sweeping changes to the United States Department of Defense since the department was established in the ...
mandated that operational control of the services follows a chain of command from the president to the secretary of defense directly to the unified combatant commanders, who have control of all armed forces units in their geographic or function area of responsibility, thus the secretaries of the military departments (and their respective service chiefs underneath them) only have the responsibility to organize, train and equip their service components. The army provides trained forces to the combatant commanders for use as directed by the secretary of defense.
 By 2013, the army shifted to six geographical commands that align with the six geographical unified combatant commands (CCMD):
* United States Army Central headquartered at Shaw Air Force Base, South Carolina
* United States Army North headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas
* United States Army South headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas
* United States Army Europe and Africa headquartered at Clay Kaserne, Wiesbaden, Germany
* United States Army Pacific headquartered at Fort Shafter, Hawaii
By 2013, the army shifted to six geographical commands that align with the six geographical unified combatant commands (CCMD):
* United States Army Central headquartered at Shaw Air Force Base, South Carolina
* United States Army North headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas
* United States Army South headquartered at Fort Sam Houston, Texas
* United States Army Europe and Africa headquartered at Clay Kaserne, Wiesbaden, Germany
* United States Army Pacific headquartered at Fort Shafter, Hawaii
 The army also transformed its base unit from divisions to brigades. Division lineage will be retained, but the divisional headquarters will be able to command any brigade, not just brigades that carry their divisional lineage. The central part of this plan is that each brigade will be modular, i.e., all brigades of the same type will be exactly the same and thus any brigade can be commanded by any division. As specified before the 2013 end-strength re-definitions, the three major types of brigade combat teams are:
* Armored brigades, with a strength of 4,743 troops as of 2014.
* Stryker brigades, with a strength of 4,500 troops as of 2014.
* Infantry brigades, with a strength of 4,413 troops as of 2014.
In addition, there are combat support and service support modular brigades. Combat support brigades include aviation (CAB) brigades, which will come in heavy and light varieties, fires (artillery) brigades (now transforms to division artillery) and expeditionary military intelligence brigades.
The army also transformed its base unit from divisions to brigades. Division lineage will be retained, but the divisional headquarters will be able to command any brigade, not just brigades that carry their divisional lineage. The central part of this plan is that each brigade will be modular, i.e., all brigades of the same type will be exactly the same and thus any brigade can be commanded by any division. As specified before the 2013 end-strength re-definitions, the three major types of brigade combat teams are:
* Armored brigades, with a strength of 4,743 troops as of 2014.
* Stryker brigades, with a strength of 4,500 troops as of 2014.
* Infantry brigades, with a strength of 4,413 troops as of 2014.
In addition, there are combat support and service support modular brigades. Combat support brigades include aviation (CAB) brigades, which will come in heavy and light varieties, fires (artillery) brigades (now transforms to division artillery) and expeditionary military intelligence brigades. Combat service support
The term combat service support (or CSS) is utilized by numerous military organizations throughout the world to describe entities that provide direct and indirect sustainment services to the groups that engage (or are potentially to be engaged) ...
brigades include sustainment brigades and come in several varieties and serve the standard support role in an army.
Combat maneuver organizations
:''To track the effects of the 2018 budget cuts, see Transformation of the United States Army#Divisions and brigades'' The U.S. Army's conventional combat capability currently consists of 11 active divisions and one deployable division headquarters (7th Infantry Division) as well as several independent maneuver units. From 2013 through 2017, the Army sustained organizational and end-strength reductions after several years of growth. In June 2013, the Army announced plans to downsize to 32 active brigade combat teams by 2015 to match a reduction in active-duty strength to 490,000 soldiers. Army chief of staff Raymond Odierno projected that the Army was to shrink to "450,000 in the active component, 335,000 in the National Guard and 195,000 in U.S. Army Reserve" by 2018. However, this plan was scrapped by the incoming Trump administration, with subsequent plans to expand the Army by 16,000 soldiers to a total of 476,000 by October 2017. The National Guard and the Army Reserve will see a smaller expansion. The Army's maneuver organization was most recently altered by the reorganization of United States Army Alaska into the11th Airborne Division
The 11th Airborne Division ("Arctic Angels") is a United States Army airborne formation, first activated on 25 February 1943, during World War II. Consisting of one parachute and two glider infantry regiments, with supporting troops, the div ...
, transferring the 1st and 4th Brigade Combat Teams of the 25th Infantry Division under a separate operational headquarters to reflect the brigades' distinct, Arctic-oriented mission. As part of the reorganization, the 1–11 (formerly 1–25) Stryker Brigade Combat Team will reorganize as an Infantry Brigade Combat Team. Following this transition, the active component BCTs will number 11 Armored brigades, 6 Stryker brigades, and 14 Infantry brigades.
Within the Army National Guard and United States Army Reserve, there are a further eight divisions, 27 brigade combat teams, additional combat support and combat service support brigades, and independent cavalry, infantry, artillery, aviation, engineer and support battalions. The Army Reserve in particular provides virtually all psychological operations and civil affairs units.
Special operations forces
, USASOC official website, dated 2018, last accessed 28 July 2019
Personnel
The Army's Talent Management Task Force (TMTF) has deployed IPPS-A, the Integrated Personnel and Pay System - Army, an app which serves the National Guard, and in 2021 the Army Reserve and Active Army. Soldiers are reminded to update their information using the legacy systems to keep their payroll and personnel information current by December 2021. IPPS-A is the Human Resources system for the Army, is now available for download for Android, or the Apple store.Army Public Affairs(2 Jun 2021) New Army pay, personnel mobile appan
unifies unit and location information for all Soldiers
using Army Organization Server data interface (AOSDI), unified with IPPS-A on the back-end. This allows aggregation of data on ACOM/ASCC, Corps, Division, Brigade, Battalion, Company, Platoon, and Squad levels It will be used for future promotions and other personnel decisions. Among the changes are: * BCAP, the Battalion Commander Assessment Program. In January 2020, over 800 majors and lieutenant colonels from all over the Army converged on Fort Knox to take part in a five-day program to select the next battalion commanders for the Army (beginning in FY2021). This process replaces the former selection process which was based solely on rank and individual reviews of past performance. From now on, more consideration will be given to an individual officer's personal preference, as part of 25 other selection criteria. "Promotion boards will now be able to see almost all substantiated adverse information". The promotion boards will be able to see anything in an officer's human resource record. Officers are encouraged to become familiar with their human resource record, and to file rebuttals to adverse information. * Depending on the success of this initiative, other assessment programs could be instituted as well, for promotion to sergeants major, and for assessment of colonels for command. Below are the U.S. Army ranks authorized for use today and their equivalent NATO designations. Although no living officer currently holds the rank of General of the Army, it is still authorized by Congress for use in wartime.
Officers
There are several paths to becoming acommissioned officer
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.
Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer, or a warrant officer. However, absent context ...
From thFuture Soldiers
Web Site. including the United States Military Academy, Reserve Officers' Training Corps, Officer Candidate School, and direct commissioning. Regardless of which road an officer takes, the insignia are the same. Certain professions including physicians, pharmacists, nurses, lawyers and chaplains are commissioned directly into the Army. Most army commissioned officers (those who are generalists)Sydney J. Freedberg Jr. (25 October 2017) Can The Pentagon Protect Young Innovators?
Fixing the 'up or out' culture, which favors generalists are promoted based on an "up or out" system. A more flexible talent management process is underway. The Defense Officer Personnel Management Act of 1980 establishes rules for the timing of promotions and limits the number of officers that can serve at any given time. Army regulations call for addressing all personnel with the rank of general as "General (last name)" regardless of the number of stars. Likewise, both colonels and lieutenant colonels are addressed as "Colonel (last name)" and first and second lieutenants as "Lieutenant (last name)".
Warrant officers
Warrant officers are single track, specialty officers with subject matter expertise in a particular area. They are initially appointed as warrant officers (in the rank of WO1) by thesecretary of the Army
The secretary of the Army (SA or SECARMY) is a senior civilian official within the United States Department of Defense, with statutory responsibility for all matters relating to the United States Army: manpower, personnel, reserve affairs, insta ...
, but receive their commission upon promotion to chief warrant officer two (CW2).
By regulation, warrant officers are addressed as "Mr. (last name)" or "Ms. (last name)" by senior officers and as "sir" or "ma'am" by all enlisted personnel. However, many personnel address warrant officers as "Chief (last name)" within their units regardless of rank.
Enlisted personnel
Sergeants and corporals are referred to as NCOs, short for non-commissioned officers.From thEnlisted Soldiers Descriptions
Web Site. This distinguishes corporals from the more numerous specialists who have the same pay grade but do not exercise leadership responsibilities. Beginning in 2021, all corporals will be required to conduct
structured self-development
The United States Army Sergeants Major Academy (USASMA) was established on 1 July 1972 at Fort Bliss, Texas, and began instruction in January 1973. Its curriculum is designed to broaden the student's current knowledge base. This approach differs ...
for the NCO ranks, completing the basic leader course (BLC), or else be laterally assigned as specialists. Specialists who have completed BLC and who have been recommended for promotion will be permitted to wear corporal rank before their recommended promotion as NCOs.
Privates and privates first class (E3) are addressed as "Private (last name)", specialists as "Specialist (last name)", corporals as "Corporal (last name)" and sergeants, staff sergeants, sergeants first class and master sergeants all as "Sergeant (last name)". First sergeants are addressed as "First Sergeant (last name)" and sergeants major and command sergeants major are addressed as "Sergeant Major (last name)".
Training
 Training in the U.S. Army is generally divided into two categories – individual and collective. Because of COVID-19 precautions, the first two weeks of basic training — not including processing and out-processing – incorporate social distancing and indoor desk-oriented training. Once the recruits have tested negative for COVID-19 for two weeks, the remaining 8 weeks follow the traditional activities for most recruits, followed by Advanced Individualized Training (AIT) where they receive training for their military occupational specialties (MOS). Some individual's MOSs range anywhere from 14 to 20 weeks of One Station Unit Training (OSUT), which combines Basic Training and AIT. The length of AIT school varies by the MOS. The length of time spent in AIT depends on the MOS of the soldier. Certain highly technical MOS training requires many months (e.g., foreign language translators). Depending on the needs of the army,
Training in the U.S. Army is generally divided into two categories – individual and collective. Because of COVID-19 precautions, the first two weeks of basic training — not including processing and out-processing – incorporate social distancing and indoor desk-oriented training. Once the recruits have tested negative for COVID-19 for two weeks, the remaining 8 weeks follow the traditional activities for most recruits, followed by Advanced Individualized Training (AIT) where they receive training for their military occupational specialties (MOS). Some individual's MOSs range anywhere from 14 to 20 weeks of One Station Unit Training (OSUT), which combines Basic Training and AIT. The length of AIT school varies by the MOS. The length of time spent in AIT depends on the MOS of the soldier. Certain highly technical MOS training requires many months (e.g., foreign language translators). Depending on the needs of the army, Basic Combat Training
Military recruit training, commonly known as basic training or boot camp, refers to the initial instruction of new military personnel. It is a physically and psychologically intensive process, which resocializes its subjects for the unique deman ...
for combat arms soldiers is conducted at a number of locations, but two of the longest-running are the Armor School and the Infantry School, both at Fort Benning
Fort Benning is a United States Army post near Columbus, Georgia, adjacent to the Alabama–Georgia border. Fort Benning supports more than 120,000 active-duty military, family members, reserve component soldiers, retirees and civilian employees ...
, Georgia. Sergeant Major of the Army Dailey notes that an infantrymen's pilot program for One Station Unit Training (OSUT) extends 8 weeks beyond Basic Training and AIT, to 22 weeks. The pilot, designed to boost infantry readiness ended in December 2018. The new Infantry OSUT covered the M240 machine gun as well as the M249 squad automatic weapon. The redesigned Infantry OSUT started in 2019. Depending on the result of the 2018 pilot, OSUTs could also extend training in other combat arms beyond the infantry. One Station Unit Training will be extended to 22 weeks for Armor by Fiscal Year 2021. Additional OSUTs are expanding to Cavalry, Engineer, and Military Police (MP) in the succeeding Fiscal Years.
A new training assignment for junior officers was instituted, that they serve as platoon leaders for Basic Combat Training (BCT) platoons. These lieutenants will assume many of the administrative, logistical, and day-to-day tasks formerly performed by the drill sergeants of those platoons and are expected to "lead, train, and assist with maintaining and enhancing the morale, welfare and readiness" of the drill sergeants and their BCT platoons. These lieutenants are also expected to stem any inappropriate behaviors they witness in their platoons, to free up the drill sergeants for training.
 The United States Army Combat Fitness Test (ACFT) was introduced in 2018 to 60 battalions spread throughout the Army. The test and scoring system is the same for all soldiers, regardless of gender. It takes an hour to complete, including resting periods. The ACFT supersedes the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT),Joe Lacdan, Army News Service (22 May 2020) SMA expects ACFT to continue as planned in COVID-19 environment
The United States Army Combat Fitness Test (ACFT) was introduced in 2018 to 60 battalions spread throughout the Army. The test and scoring system is the same for all soldiers, regardless of gender. It takes an hour to complete, including resting periods. The ACFT supersedes the Army Physical Fitness Test (APFT),Joe Lacdan, Army News Service (22 May 2020) SMA expects ACFT to continue as planned in COVID-19 environment"Soldiers can use their last APFT score to remain promotion eligible." as being more relevant to survival in combat. Six events were determined to better predict which muscle groups of the body were adequately conditioned for combat actions: three deadlifts, a standing power throw of a ten-pound medicine ball, hand-release pushups (which replace the traditional pushup), a sprint/drag/carry 250 yard event, three pull-ups with leg tucks (or a plank test in lieu of the leg tuck), a mandatory rest period, and a two-mile run. As of 1 October 2020 all soldiers from all three components (Regular Army, Reserve, and National Guard) are subject to this test. The ACFT now tests all soldiers in basic training as of October 2020. The ACFT became the official test of record 1 October 2020; before that day every Army unit was required to complete a diagnostic ACFTMaj. Stephen Martin (December 27, 2019) Kentucky Guard first to receive ACFT equipment
"36,608 ACFT sets for the total army by May 15". "The Army is focused on the tactical athlete".
Staff Sgt. Warren Wright (10 January 2020) NY National Guard finds creative ways to train for new fitness test
"finding creative ways to exercise at home and on their own time" (All Soldiers with valid APFT scores can use them until March 2022. The Holistic Health and Fitness (H2F) System is one way that soldiers can prepare.).US Army (2020) US Army soldier prepares for ACFT
Learning how to retrain an injured body; using resistance bands (good for leg tucks); know your limits; use out-training (see video for sample); practice technique (good for deadlift, and power throw)Haley Britzk
(27 Oct 2021) This is the Army's plan to stop physically breaking so many of its soldiers
Sexual Harassment/Assault Response & Prevention (SHARP) office is located in Falcon
Holistic Health and Fitness
Holism () is the idea that various systems (e.g. physical, biological, social) should be viewed as wholes, not merely as a collection of parts. The term "holism" was coined by Jan Smuts in his 1926 book ''Holism and Evolution''."holism, n." OED Onl ...
Center (H2F) at Fort Bragg The ACFT movements directly translate to movements on the battlefield.
Following their basic and advanced training at the individual level, soldiers may choose to continue their training and apply for an "additional skill identifier" (ASI). The ASI allows the army to take a wide-ranging MOS and focus it on a more specific MOS. For example, a combat medic, whose duties are to provide pre-hospital emergency treatment, may receive ASI training to become a cardiovascular specialist, a dialysis specialist, or even a licensed practical nurse. For commissioned officers, training includes pre-commissioning training, known as Basic Officer Leader Course A, either at USMA or via ROTC
The Reserve Officers' Training Corps (ROTC ( or )) is a group of college- and university-based officer-training programs for training commissioned officers of the United States Armed Forces.
Overview
While ROTC graduate officers serve in all ...
, or by completing OCS. After commissioning, officers undergo branch-specific training at the Basic Officer Leaders Course B, (formerly called Officer Basic Course), which varies in time and location according to their future assignments. Officers will continue to attend standardized training at different stages of their careers.
 Collective training at the unit level takes place at the unit's assigned station, but the most intensive training at higher echelons is conducted at the three combat training centers (CTC); the National Training Center (NTC) at Fort Irwin, California, the Joint Readiness Training Center (JRTC) at Fort Polk, Louisiana and the
Collective training at the unit level takes place at the unit's assigned station, but the most intensive training at higher echelons is conducted at the three combat training centers (CTC); the National Training Center (NTC) at Fort Irwin, California, the Joint Readiness Training Center (JRTC) at Fort Polk, Louisiana and the Joint Multinational Training Center
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
(JMRC) at the Hohenfels Training Area in Hohenfels and Grafenwöhr, Germany. ReARMM is the Army Force Generation process approved in 2020 to meet the need to continuously replenish forces for deployment, at unit level and for other echelons as required by the mission. Individual-level replenishment still requires training at a unit level, which is conducted at the continental U.S. (CONUS) replacement center (CRC) at Fort Bliss, in New Mexico and Texas before their individual deployment.
Chief of Staff Milley notes that the Army is suboptimized for training in cold-weather regions, jungles, mountains, or urban areas where in contrast the Army does well when training for deserts or rolling terrain. Post 9/11, Army unit-level training was for counter-insurgency (COIN); by 2014–2017, training had shifted to decisive action training.
Equipment
The chief of staff of the Army has identified six modernization priorities, in order: artillery, ground vehicles, aircraft, network, air/missile defense, and soldier lethality.ASA(ALT)
The Office of the United States Assistant Secretary of the Army for Acquisition, Logistics, and Technology (ASA(ALT) pronounced ''A-salt'') is known as OASA(ALT). OASA(ALT) serves, when delegated, as the Army Acquisition Executive, the Senior Pr ...
br>Weapon Systems Handbook 2018Page 32 lists how this handbook is organized. 440 pages.
Weapons
Individual weapons
The United States Army employs various weapons to provide light firepower at short ranges. The most common weapon type used by the army is the M4 carbine, a compact variant of the M16 rifle, along with the 7.62×51mm variant of the FN SCAR for Army Rangers. The primary sidearm in the U.S. Army is the 9 mm M9 pistol; theM11 pistol M11 or M-11 may refer to:
Aviation
* Miles M.11 Whitney Straight, a 1936 two-seater light aircraft
* Shvetsov M-11, an aircraft engine produced in the Soviet Union
Science
* Messier 11 (M11), an open star cluster also known as the Wild Duck Cl ...
is also used. Both handguns are to be replaced by the M17 through the Modular Handgun System program. Soldiers are also equipped with various hand grenade
A grenade is an explosive weapon typically thrown by hand (also called hand grenade), but can also refer to a shell (explosive projectile) shot from the muzzle of a rifle (as a rifle grenade) or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade genera ...
s, such as the M67 fragmentation grenade and M18 smoke grenade
The M18 Colored Smoke Grenade is a US Army grenade used as a ground-to-ground or ground-to-air signaling device, a target or landing zone marking device, or a screening device for unit maneuvering.
History
The M18 was developed in 1942 during ...
.
Many units are supplemented with a variety of specialized weapons, including the M249 SAW (Squad Automatic Weapon), to provide suppressive fire at the squad level. Indirect fire is provided by the M320 grenade launcher. The M1014 Joint Service Combat Shotgun or the Mossberg 590 Shotgun are used for door breaching and close-quarters combat. The M14EBR is used by designated marksmen. Snipers use the M107 Long Range Sniper Rifle
The Barrett M82 (standardized by the U.S. military as the M107) is a recoil-operated, semi-automatic anti-materiel rifle developed by the American company Barrett Firearms Manufacturing.
Also called the Light Fifty (due to its chambering o ...
, the M2010 Enhanced Sniper Rifle and the M110 Semi-Automatic Sniper Rifle.
Crew-served weapons
The army employs various crew-served weapons to provide heavy firepower at ranges exceeding that of individual weapons. The M240 is the U.S. Army's standard Medium Machine Gun. The M2 heavy machine gun is generally used as a vehicle-mounted machine gun. In the same way, the 40 mm MK 19 grenade machine gun is mainly used by motorized units. The U.S. Army uses three types of mortar for indirect fire support when heavier artillery may not be appropriate or available. The smallest of these is the 60 mm M224, normally assigned at the infantry company level. At the next higher echelon, infantry battalions are typically supported by a section of 81 mm M252 mortars. The largest mortar in the army's inventory is the 120 mm M120/M121, usually employed by mechanized units. Fire support for light infantry units is provided by towed howitzers, including the 105 mm M119A1 and the 155 mm M777. The U.S. Army utilizes a variety of direct-fire rockets and missiles to provide infantry with an Anti-Armor Capability. The AT4 is an unguided projectile that can destroy armor and bunkers at ranges up to 500 meters. The FIM-92 Stinger is a shoulder-launched, heat seeking anti-aircraft missile. The FGM-148 Javelin and BGM-71 TOW are anti-tank guided missiles.Vehicles
 U.S. Army doctrine puts a premium on mechanized warfare. It fields the highest vehicle-to-soldier ratio in the world as of 2009. The army's most common vehicle is the High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV), commonly called the Humvee, which is capable of serving as a cargo/troop carrier, weapons platform and ambulance, among many other roles. While they operate a wide variety of combat support vehicles, one of the most common types centers on the family of HEMTT vehicles. The M1A2 Abrams is the army's main battle tank, while the
U.S. Army doctrine puts a premium on mechanized warfare. It fields the highest vehicle-to-soldier ratio in the world as of 2009. The army's most common vehicle is the High Mobility Multipurpose Wheeled Vehicle (HMMWV), commonly called the Humvee, which is capable of serving as a cargo/troop carrier, weapons platform and ambulance, among many other roles. While they operate a wide variety of combat support vehicles, one of the most common types centers on the family of HEMTT vehicles. The M1A2 Abrams is the army's main battle tank, while the M2A3 Bradley
The M2 Bradley, or Bradley IFV, is an American infantry fighting vehicle that is a member of the Bradley Fighting Vehicle family. It is manufactured by BAE Systems Land & Armaments, which was formerly United Defense.
The Bradley is designed for ...
is the standard infantry fighting vehicle
An infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), also known as a mechanized infantry combat vehicle (MICV), is a type of armoured fighting vehicle used to carry infantry into battle and provide direct-fire support. The 1990 Treaty on Conventional Armed Forc ...
. Other vehicles include the Stryker, the M113 armored personnel carrier and multiple types of Mine Resistant Ambush Protected (MRAP) vehicles.
 The U.S. Army's principal artillery weapons are the
The U.S. Army's principal artillery weapons are the M109A6 Paladin M1, M01 or M-1 may refer to:
Arts, entertainment & media
* WD-M01 Turn A Gundam, a mecha from the anime ''Turn A Gundam''
* M-1 (rapper), one half of hip hop duo Dead Prez
* Korg M1, a keyboard synthesizer
* Leica M1, a 1959 35 mm camer ...
self-propelled howitzer and the M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS), both mounted on tracked platforms and assigned to heavy mechanized units.
Aviation
While the United States Army Aviation Branch operates a fewfixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinc ...
, it mainly operates several types of rotary-wing aircraft. These include the AH-64 Apache attack helicopter
An attack helicopter is an armed helicopter with the primary role of an attack aircraft, with the offensive capability of engaging ground targets such as enemy infantry, military vehicles and fortifications. Due to their heavy armament they ...
, the UH-60 Black Hawk utility tactical transport helicopter and the CH-47 Chinook heavy-lift transport helicopter. Restructuring plans call for reduction of 750 aircraft and from 7 to 4 types. The Army is evaluating two fixed-wing aircraft demonstrators; ARES, and Artemis are under evaluation to replace the Guardrail ISR (Intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance) aircraft. Under the Johnson-McConnell agreement of 1966, the Army agreed to limit its fixed-wing aviation role to administrative mission support (light unarmed aircraft which cannot operate from forward positions). For UAVs, the Army is deploying at least one company of drone MQ-1C Gray Eagle
The General Atomics MQ-1C Gray Eagle (previously the Warrior; also called Sky Warrior and ERMP or Extended-Range Multi-Purpose) is a medium-altitude, long-endurance (MALE) unmanned aircraft system (UAS). It was developed by General Atomics Aero ...
s to each Active Army division.
Uniforms
 The Army Combat Uniform (ACU) currently features a camouflage pattern known as Operational Camouflage Pattern (OCP); OCP replaced a pixel-based pattern known as Universal Camouflage Pattern (UCP) in 2019.
The Army Combat Uniform (ACU) currently features a camouflage pattern known as Operational Camouflage Pattern (OCP); OCP replaced a pixel-based pattern known as Universal Camouflage Pattern (UCP) in 2019.
 On 11 November 2018, the Army announced a new version of 'Army Greens' based on uniforms worn during World War II that will become the standard garrison service uniform. The blue Army Service Uniform will remain as the dress uniform. The Army Greens are projected to be first fielded in the summer of 2020.
On 11 November 2018, the Army announced a new version of 'Army Greens' based on uniforms worn during World War II that will become the standard garrison service uniform. The blue Army Service Uniform will remain as the dress uniform. The Army Greens are projected to be first fielded in the summer of 2020.
Berets
 The beret flash of enlisted personnel displays their
The beret flash of enlisted personnel displays their distinctive unit insignia
A distinctive unit insignia (DUI) is a metallic Heraldry, heraldic badge or device worn by soldiers in the United States Army. The DUI design is derived from the coat of arms authorized for a unit. DUIs may also be called "distinctive insignia" (D ...
(shown above). The U.S. Army's black beret is no longer worn with the ACU for garrison duty, having been permanently replaced with the patrol cap. After years of complaints that it was not suited well for most work conditions, Army Chief of Staff General Martin Dempsey
Martin “Marty” Edward Dempsey (born March 14, 1952), is a retired United States Army general who served as the 18th chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff from October 1, 2011 until September 25, 2015. He previously served as the 37th chief o ...
eliminated it for wear with the ACU in June 2011. Soldiers who are currently in a unit in jump status still wear berets, whether the wearer is parachute-qualified or not (maroon beret), while members of Security Force Assistance Brigade
A Security Force Assistance Brigade (SFAB) (pronounced ) is a specialized United States Army unit formed to conduct security force assistance (SFA) missions: to train, advise, assist, enable and accompany operations with allied and partner nati ...
s (SFABs) wear brown berets. Members of the 75th Ranger Regiment and the Airborne and Ranger Training Brigade (tan beret) and Special Forces (rifle green beret) may wear it with the Army Service Uniform for non-ceremonial functions. Unit commanders may still direct the wear of patrol caps in these units in training environments or motor pools.
Tents
The Army has relied heavily ontent
A tent () is a shelter consisting of sheets of fabric or other material draped over, attached to a frame of poles or a supporting rope. While smaller tents may be free-standing or attached to the ground, large tents are usually anchored using gu ...
s to provide the various facilities needed while on deployment (Force Provider Expeditionary (FPE)). The most common tent uses for the military are as temporary barracks
Barracks are usually a group of long buildings built to house military personnel or laborers. The English word originates from the 17th century via French and Italian from an old Spanish word "barraca" ("soldier's tent"), but today barracks are u ...
(sleeping quarters), DFAC buildings (dining facilities),Accomplishes paperwork reduction based on reading each soldier's Common Access Card at each use at DFAC.
Natick Soldier Systems Center
Natick ( ) is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. It is near the center of the MetroWest region of Massachusetts, with a population of 37,006 at the 2020 census. west of Boston, Natick is part of the Greater Boston are ...
. Each FPE contains billeting, latrines, showers, laundry and kitchen facilities for 50–150 Soldiers, and is stored in Army Prepositioned Stocks 1, 2, 4 and 5. This provisioning allows combatant commanders to position soldiers as required in their Area of Responsibility
Area of responsibility (AOR) is a pre-defined geographic region assigned to Combatant commanders of the Unified Command Plan (UCP), that are used to define an area with specific geographic boundaries where they have the authority to plan and cond ...
, within 24 to 48 hours.
The U.S. Army is beginning to use a more modern tent called the deployable rapid assembly shelter (DRASH). In 2008, DRASH became part of the Army's Standard Integrated Command Post System.NG, DHS Technologies to support SICPS/TMSSUnited Press International
See also
* '' America's Army'' (video games for recruitment) *Army CHESS
Army CHESS (Computer Hardware Enterprise Software and Solutions) is the main provider of commercial enterprise Information Technology, information technology (IT) solutions, computer software, and Computer hardware, hardware for the United States ...
(Computer Hardware Enterprise Software and Solutions)
* History of the United States Army
* List of military weapons of the United States
* Junior Reserve Officers' Training Corps
* List of active United States military aircraft
* List of comparative military ranks
* List of former United States Army medical units
* List of wars involving the United States
* Reorganization plan of United States Army
The reorganization plan of the United States Army is a current modernization (2017–2028) and reorganization (2006–2016) plan of the United States Army that was implemented (2006–2016) under the direction of Brigade Modernization Command.
This ...
* Soldier's Creed
The Soldier's Creed is a standard by which all United States Army personnel are expected to live. All U.S. Army enlisted personnel are taught the Soldier's Creed during basic training, and recite the creed in public ceremonies at the conclusion o ...
* Timeline of United States military operations
This timeline of United States government military operations, based in part on reports by the Congressional Research Service, shows the years and places in which U.S. military units participated in armed conflicts or occupation of foreign territ ...
* United States Army Basic Training
* U.S. Army Combat Arms Regimental System
* U.S. Army Regimental System
* Vehicle markings of the United States military
United States Army vehicles must be marked with a unit designation to foster accountability and promote attention to detail during maintenance operations. The term "bumper number" refers the combination of numbers and letters on the front and rear ...
Notes
References
*Further reading
* * Bailey, Beth. ''America's Army: Making the All-Volunteer Force'' (2009) * * Chambers, John Whiteclay, ed. ''The Oxford Guide to American Military History'' (1999) online at many libraries * Clark, J. P. ''Preparing for War: The Emergence of the Modern U.S. Army, 1815–1917'' (Harvard UP, 2017) 336 pp. * Coffman, Edward M. ''The War to End All Wars: The American Military Experience in World War I'' (1998), a standard history * Kretchik, Walter E. ''U.S. Army Doctrine: From the American Revolution to the War on Terror'' (University Press of Kansas; 2011) 392 pages; studies military doctrine in four distinct eras: 1779–1904, 1905–1944, 1944–1962, and 1962 to the present. * Woodward, David R. ''The American Army and the First World War'' (Cambridge University Press, 2014). 484 pponline review
External links
* * * *Army.mil/photos
– United States Army featured photos
U.S. Army Collection
– Missouri History Museum
(compiled by the United States Army Center of Military History)
US-militaria.com
– The U.S. Army during the Second World War {{DEFAULTSORT:United States Army Uniformed services of the United States Military units and formations established in 1775 1775 establishments in the Thirteen Colonies United States Armed Forces service branches